Introduction
Uttar Pradesh is a prosperous state from the point of view of agriculture and animal husbandry due to favourable geographical structures. According to the 2011 census, 59.3 percent of the total working population of the state is employed in agriculture and allied sectors. Out of this, 29.0% are farmers and 30.3% are agricultural labourers.
In the year 2022-23, the contribution of agriculture in the gross state domestic product of the state is 26%, and in the year 2022-23, the agricultural growth rate has become 18.2%. That is why agriculture is called the backbone of the economy in UP. Uttar Pradesh ranks first among all the states in the country’s total food grain production.
Types of farming
On the basis of main source of moisture for crops, the farming can be classified as :
- Irrigated
- Protective farming
- Productive farming
- Rainfed ( barani )
- Dryland farming
- Wetland farming
- Irrigated farming : There is difference in the nature of irrigated farming as well on on objective of irrigation, protective or productive.
- The objective of protective irrigation is to protect the crops from adverse effects of soil moisture deficiency which often means that irrigation acts as a supplementary source of water over and above the rainfall. The strategy of this kind of irrigation is to provide soil moisture to maximum possible area.
- Productive irrigation is meant to provide sufficient soil moisture in the cropping season to achieve high productivity. In such irrigation the water input per unit area of cultivated land is higher than protective irrigation.
- Rainfed ( barani ) farming : Rainfed farming is further classified on the basis of adequacy of soil moisture during cropping season into dryland and wetland farming.
- In India, the dryland farming is largely confined to the regions having annual rainfall less than 75 cm. These regions grow hardy and drought resistant crops such as ragi, bajra, moong, gram and guar (fodder crops) and practise various measures of soil moisture conservation and rain water harvesting.
- In wetland farming, the rainfall is in excess of soil moisture requirement of plants during rainy season. Such regions may face flood and soil erosion hazards. These areas grow various water intensive crops such as rice, jute and Sugarcane and practise aquaculture in the fresh water bodies.
Classification of Crop
The crops are classified as :
- Food grains
- cereals and millets,
- pulses, and
- fruits and vegetables (often called horticultural crops).
- Non-food grains.
- Oilseeds,
- fiber crops,
- many plantation crops and
- fodder crops.
Cereals, millets and pulses are collectively called food grains.
Production of agricultural crops in UP
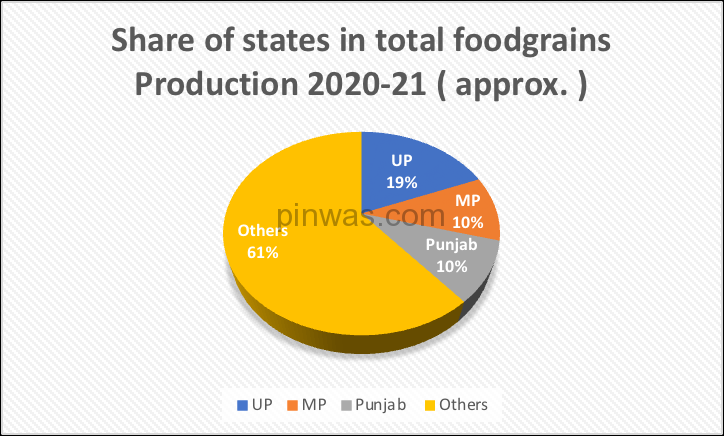
According to the fourth forecast, the total food grain production in 2021-22 is estimated at 315.7 million tonnes, out of which UP alone is at the first place with a contribution of 56.11 million tonnes, which is 17.77% of India’s total food grain production.
- Foodgrains : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 129.34 ( 100 % ) | 308.65 ( 100 % ) | 2386 | 54.32 % |
| UP | 19.93 ( 15.41 % ) | 58.32 ( 18.89 % ) | 2926 | 81.3 % |
| Top states | 1. UP 2. Rajasthan 3. MP | 1. UP 2. MP 3. Rajasthan | 1. Punjab 2. Haryana 3. Telangana | 1. Punjab 2. Haryana 3. UP |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh ranks first in the country in terms of area under food grains.
- UP ranks first in the country in food grain production.
- Uttar Pradesh ranks third in terms of area under irrigation.
Rice ( Oriza sativa )
Rice is commonly grown in areas with 125 to 200 cm of rainfall and temperatures above 23 °C. It is also cultivated with the help of irrigation in areas with low rainfall and high temperature. Rice grows in all type of soil, however, soil capable of holding water for a longer period such as heavy soil ( clay, clay-loamy and loamy ) are most suited for its cultivation.
Due to sufficient rainfall in the eastern and Terai part of the state, rice is cultivated normally here. Along with this, it is also cultivated in the southern and western parts where there is irrigation facility.
Districts famous for rice cultivation in the state are — Maharajganj, Siddharthnagar, Kushinagar, Deoria, Gorakhpur, Basti, Gonda, Bahraich, Shravasti, Balrampur, Lakhimpur, Pilibhit, Saharanpur, Mau, Ballia, Varanasi, Prayag, Lucknow etc. districts.
Siddharthnagar is famous for fragrant rice Kalanamak. Kalanamak rice granted GI tag by Government of India in 2012.
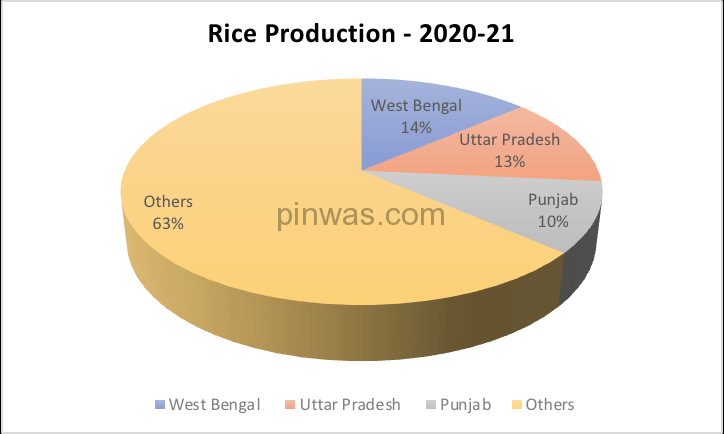
As per the fourth forecast, the total rice production in 2021-22 is estimated at 130.3 million tonnes. Out of this, Uttar Pradesh alone ranks second with a production of 15.27 million tonnes, which is 11.72 % of the country’s total production.
- Rice : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 45.07 ( 100 % ) | 122.87 ( 100 % ) | 2713 | 62.7 % |
| UP | 5.68 ( 12.6 % ) | 15.66 ( 12.81 % ) | 2749 | 86.3 % |
| Top states | 1. UP 2. West Bengal 3. Odisa | 1. West Bengal 2. MP 3. Punjab | 1. Punjab 2. Andhra Pradesh 3. Rajasthan | 1. Punjab 2. Telangana 3. Andhra Pradesh |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is first in area under rice cultivation.
- West Bengal is first in rice production.
- Punjab ranks first in terms of productivity & the irrigated area of rice sown.
Wheat ( Triticum aestivum )
Environmental requirements : Wheat is primarily a crop of temperate zone. Hence, its cultivation in state ( and India ) done during winter, i.e. Rabi season. That’s why it is sown in October-November and harvested in March-April.
- Rainfall – 50 to 75 cm.
- Temperature : at the time of sowing 10 to 15 °C, at harvest time about 25 °C. Thus it requires a temperature of 10 to 25 °C.
Wheat is cultivated in the state everywhere except the hilly and plateau areas. The Ganga-Ghaghra Doab region has the highest productivity in the state.
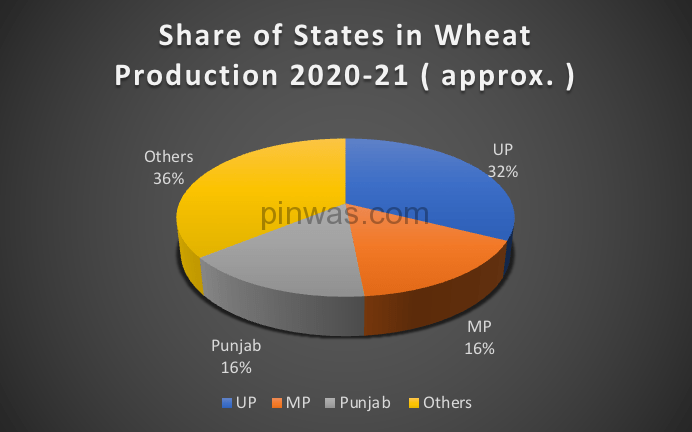
As per the fourth forecast, the total wheat production in 2021-22 is estimated at 106.8 million tonnes. Out of this, Uttar Pradesh alone ranks first with a production of 33.95 million tonnes, which is 31.77% of the country’s total production.
- Wheat : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 31.61 ( 100 % ) | 109.5 ( 100 % ) | 3464 | 95.3 % |
| UP | 9.85 ( 31.16 % ) | 35.50 ( 32.42 % ) | 3604 | 99 % |
| Top states | 1. UP 2. MP 3. Punjab | 1. UP 2. MP 3. Punjab | 1. Punjab 2. Haryana 3. Rajasthan | 1. Haryana 2. Rajasthan 3. Punjab 4. UP |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is first in area under wheat cultivation.
- Uttar Pradesh is first in wheat production.
- UP ranks fourth in the irrigated area of wheat sown.
Maize or Corn ( Zea mays )
Maize requires average temperature between 21°C and 27°C. Temperature below 10°C or above 35°C is harmful for the crop. It performs well in the region where the rainfall is between 50-75 cm Bright sunshine after rainfall is useful for healthy growth of the crop.
Maize is cultivated mainly as a kharif crop, while it is also grown as a rabi crop.
It is a food as well as fodder crop, but is also used as a raw material for industries.
It is cultivated in Meerut, Farrukhabad, Ghaziabad, Gonda, Bulandshahr, Bahraich, Jaunpur, Firozabad, Etah, Mainpuri, etc. districts of the state.
- Maize : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 9.86 ( 100 % ) | 31.51 ( 100 % ) | 3195 | 26.28 % |
| UP | 0.77 ( 7.85 % ) | 1.80 ( 5.72 % ) | 2331 | 47.7 % |
| Top states | 1. Karnataka 2. MP 3. Maharashtra | 1. Karnataka 2. MP 3. Maharashtra 9th. UP | 1. Tamil Nadu 2. Telangana 3. West Bengal | 1. West Bengal 2. Andhra Pradesh 3. Punjab 4. Bihar |
Nutri/Coarse Cereals
Millets are group of small grained cereal food crops which are highly tolerant to drought and other extreme weather conditions and are grown with low chemical inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides.
Most of millet crops are native of India and are popularly known as Nutri-cereals as they provide most of the nutrients required for normal functioning of human body.
Nutri/Coarse Cereals are classified into Major Millets and Minor Millets based on their grain size.
Nutri or Coarse Cereals are classified as follow :
- Major Millets –
- Sorghum ( Jowar )
- Pearl Millet ( Bajra )
- Finger Millet ( Ragi or Mandua )
- Minor Millets –
- Little Millet ( Kutki )
- Kodo Millet ( Kodo )
- Barnyard Millet ( Sawa or Jhangora )
- Foxtail Millet ( Kangni or Kakun )
- Proso Millet ( Cheena )
Psuedo Millets : Millets that are not from the grass family but are used in the same way are called pseudo millets. These are – Buck-wheat ( Kuttu ), Amarnath ( Chaulai ).
The International Year of Millets – 2023 The United Nations General Assembly, in its 75th session during March 2021, declared 2023 the International Year of Millets (IYM). Millets are Smart Food with high nutritional value, are climate resilient, and align with several UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These are also important by virtue of their mammoth potential to generate livelihood, increase farmers’ income and ensure food & nutritional security all over the world. |
- Nutri/Coarse Cereals : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 28.83 ( 100 % ) | 51.15 ( 100 % ) | 2146 | — |
| UP | 2.02 ( 8.49 % ) | 4.59 ( 8.97 % ) | 2266 | — |
| Top states | 1. Rajasthan 2. Maharashtra 3. Karnataka | 1. Rajasthan 2. Karnataka 3. Maharashtra 5th – UP | 1. West Bengal 2. Telangana 3. Andhra Pradesh | — |
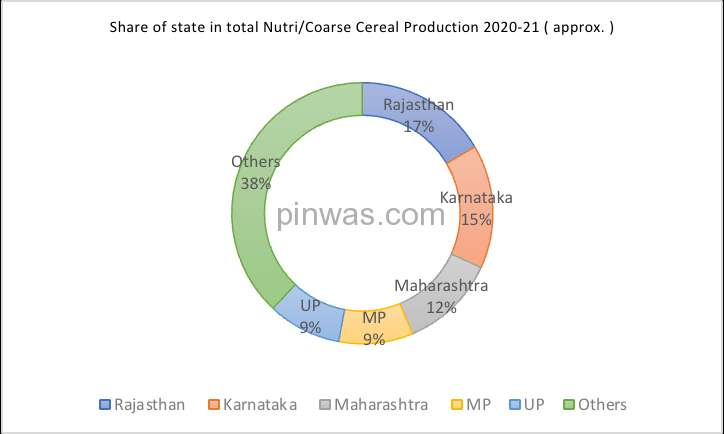
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is 5th in total Nutri/Coarse Cereals production.
Jowar ( Sorghum bicolor )
- Jowar : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 4.24 ( 100 % ) | 4.78 ( 100 % ) | 1128 | 10.1 % |
| UP | 0.17 ( 4.10 % ) | 0.27 ( 5.74 % ) | 1578 | 6.1 |
| Top states | 1. Maharashtra 2. Karnataka 3. Rajasthan | 1. Maharashtra 2. Karnataka 3. Rajasthan | 1. Andhra Pradesh 2. Telangana 3. MP 4. UP | 1. Andhra Pradesh 2. Telangana 3. Tamil Nadu |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is 4th in term of productivity jowar in the country.
Pearl-Millet ( Pennisetum typhoideum )
Bajra ( Pearl-Millet ) grows well in the region where the temperature varies between 25 to 30 °C. The crop requires about 30 to 50 cm ( i.e. less than 50 cm ) of annual rainfall. Heavy rainfall exceeding 75 cm is however, unsuitable for the Bajra crop. It is the most drought-and heat tolerant crop with highest water-use efficiency. The crop is grown mostly during kharif season from June to October.
Agra, Mathura, Badaun, Aligarh, Moradabad, Etah, Firozabad, Mainpuri, Etawah, Shahjahanpur, Pratapgarh, Ghazipur, Farrukhabad and Kanpur are the main millet producing districts in the state.
- Bajra : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 7.57 ( 100 % ) | 10.86 ( 100 % ) | 1436 | 9.4 % |
| UP | 0.91 ( 11.99 % ) | 2.01 ( 18.54 % ) | 2221 | 15.1 % |
| Top states | 1. Rajasthan 2. UP 3. Haryana | 1. Rajasthan 2. UP 3. Haryana | 1. Haryana 2. MP 3. UP | 1. Haryana 2. Gujarat 3. Karnataka 4. UP |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is 2nd in area under bajra cultivation.
- Uttar Pradesh is 2nd in bajra production.
- UP ranks 3rd in terms of productivity.
- UP ranks 4th in the irrigated area of bajra sown.
Barley ( Hordeum vulgare)
Barley cultivation is done in dry and alluvial soil areas of the state. Barley requires the same conditions as wheat in terms of temperature, water, planting and harvesting.
Pulses
- Total Pulses : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 28.83 ( 100 % ) | 25.72 ( 100 % ) | 892 | 23.2 % |
| UP | 2.38 ( 8.24 % ) | 2.56 ( 9.97 % ) | 1079 | 27.6 % |
| Top states | 1. Rajasthan 2. MP 3. Maharashtra | 1. MP 2. Rajasthan 3. Maharashtra 4. UP | 1. Gujarat 2. MP & Jharkhand 3. UP | 1. MP 2. UP 3. Rajasthan |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is fourth in total pulses production.
- UP ranks second in the irrigated area of total pulses sown.
Gram ( Cicer arietinum )
Gram is cultivated in sub-tropical areas. It is mostly a rainfed crop cultivated during Rabi season.
It requires less fertile soil, 30 to 50 cm rainfall, and 15 to 25°C temperature at the time of sowing. Therefore, it is cultivated in those areas of the state where dry and light soil is found.
Gram is cultivated in the state in the districts of Chitrakoot, Mahoba, Banda, Hamirpur, Barabanki, Sonbhadra, Kanpur, Fatehpur, Jalaun, Lalitpur, Jhansi, Agra etc. Most gram is grown in Bundelkhand region.
- Gram : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 9.85 ( 100 % ) | 11.99 ( 100 % ) | 1217 | 49.6 % |
| UP | 0.61 ( 6.20 % ) | 0.84 ( 7.01 % ) | 1376 | 24.6 % |
| Top states | 1. Maharashtra 2. Rajasthan 3. MP | 1. MP 2. Maharashtra 3. Rajasthan 4. Gujarat 5. UP | 1. Gujarat 2. MP 3. UP | 1. MP 2. Rajasthan 3. Chhattisgarh |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is fifth in Gram production.
- UP ranks third in productivity of Gram.
Pigeon-pea or Arhar / Tur ( Cajanus cajan)
Pigeon-pea is native crop of India. It is also known as red gram. Arhar is cultivated in wide range of climatic conditions in tropical and sub-tropical areas with temperature range of 20 to 35 °C. The plant is sensitive to frost during stage of growth.
Arhar is a kharif crop which requires high temperature for sowing and harvesting and low temperature for pod formation and ripening. Well drained soil is good for pigeon pea cultivation. It is sown in June-July and harvested in March-April. Sandy loam soil is suitable for this.
Prayagraj, Fatehpur Chitrakoot, Hamirpur, Mahoba, Banda, Jhansi, Lucknow, Lalitpur are the major Arhar producing districts of the state.
U.P. ranks third in the country in Arhar production. According to the fourth advance estimate, the state has a share of 8% in the country’s total production (4.3 million tonnes) with 0.35 million tonnes in 2021-22. ( Source : Economic Survey 2022-23 )
- Tur/Arhar : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 4.88 ( 100 % ) | 4.28 ( 100 % ) | 892 | 5.2 % |
| UP | 0.30 ( 6.16 % ) | 0.29 ( 6.83 % ) | 988 | 13.5 % |
| Top states | 1. Karnataka 2. Maharashtra 3. Telangana 4. UP | 1. Maharashtra 2. Karnataka 3. Telangana 4.. UP | 1. Jharkhand 2. MP 3. Gujarat | 1. UP 2. Karnataka 3. Gujarat |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is foruth in area under Tur/Arhar cultivation.
- UP ranks fourth in productivity of Tur/Arhar.
- UP ranks first in area under irrigation.
Lentil/ Masur ( Lens culinaris )
- Lentil : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 1.45 ( 100 % ) | 1.45 ( 100 % ) | 1001 | — |
| UP | 0.47 ( 32.62 % ) | 0.47 ( 32.20 % ) | 998 | — |
| Top states | 1. MP 2. UP 3. West Bengal | 1. MP 2. UP 3. West Bengal | 1. MP 2. UP 3. Jharkhand | — |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is second in Area under cultivation, production & productivity of Lentil.
Nine Oilseeds
- Nine Oilseeds : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 28.79 ( 100 % ) | 36.10 ( 100 % ) | 1254 | 31.4 % |
| UP | 1.20 ( 4.16 % ) | 1.26 ( 3.49 % ) | 1054 | 41.8 % |
| Top states | 1. MP 2. Rajasthan 3. Maharashtra | 1. Rajasthan 2. Maharashtra 3. MP | 1. Tamil Nadu 2. Haryana 3. Gujarat | 1. West Bengal 2. Haryana 3. Rajasthan |
Mustard ( Brassica juncea ) & Rapeseed ( Brassica rapa )
Mustard is cultivated in the state either independently or in mixed form with wheat, peas and barley. Mustard is cultivated in all parts of the state, but specially in central and western UP.
The rapeseed and mustard crops are sub-tropical crops cultivated during Rabi season. It is sown in September-October and harvested in February-March. The rapeseed & mustard grow well in the area having 25 to 40 cm of rainfall.
- Rapeseed & Mustard : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 6.69 ( 100 % ) | 10.11 ( 100 % ) | 1511 | 83.2 % |
| UP | 0.70 ( 10.48 % ) | 0.99 ( 9.79 % ) | 1412 | 83.3 % |
| Top states | 1. Rajasthan 2. MP 3. UP | 1. Rajasthan 2. MP 3. Haryana 4. UP | 1. Haryana 2. Gujarat 3. MP | 1. Gujarat 2. Rajasthan 3. West Bengal |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is third in Area under Rapeseed & Mustard cultivation.
- UP ranks fourth in Rapeseed & Mustard production.
Groundnut ( Arachis hypogaea )
Groundnut is basically a kharif crop, which is sown in June-July and is dug in November-December. Sandy soil is suitable for this. Small quantity of groundnut is cultivated in Sitapur, Hardoi, Etah, Badayun, Mainpuri, Moradabad etc. districts of the state.
- Groundnut : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 6.09 ( 100 % ) | 10.21 ( 100 % ) | 1676 | 30.9 % |
| UP | — | — | — | — |
| Top states | 1. Gujarat 2. Andhra Pradesh 3. Rajasthan | 1. Gujarat 2. Rajasthan 3. Tamil Nadu | 1. Tamil Nadu 2. Rajasthan 3. Gujarat | 1. Rajasthan 2. Tamil Nadu 2. Karnataka |
Sugarcane ( Saccharum officinarum )
Sugarcane is a tropical and sub-tropical crop. India is considered the origin of sugarcane. It is a perennial crop. It required well-drained land, heavy loamy fertile soil, abundant supply of moisture, frost-free weather and a large number of labourers. Sugarcane is an irrigated crop. Sugarcane requires 20 to 26°C temperature and 100 to 200 cm rainfall.
It is the most important cash crop of the state. There are two main areas of sugarcane production in the state- (1) Terai region and (2) Doab region of Ganga-Yamuna. Meerut, Muzaffarnagar, Ghaziabad, Rampur, Bareilly, Sitapur, Lakhimpur, Pilibhit, Bulandshahr, Aligarh, Moradabad, Ballia, Deoria, Mau, Azamgarh, Ayodhya and Gorakhpur are the major sugarcane producing districts of the state.
U.P. ranks first in the country in sugarcane production. According to the fourth advance estimate, the state’s contribution to the country’s total sugarcane production (431.8 million tonnes) in 2021-22 is 41.09% with 177.43 million tonnes.
- Sugarcane : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 4.86 ( 100 % ) | 399.25 ( 100 % ) | 82205 | 96.6 % |
| UP | 2.18 ( 44.89 % ) | 177.67 ( 44.50 % ) | 81500 | 96.2 % |
| Top states | 1. UP 2. Maharashtra 3. Karnataka | 1. UP 2. Maharashtra 3. Karnataka | 1. Tamil Nadu 2. Karnataka 3. Maharashtra |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is first in Area under Sugarcane cultivation.
- UP ranks first in Sugarcane production.
UP vs Maharashtra : It is to be noted here that sugarcane production and sugar production are two different things. It is not necessary that the state which is first in sugarcane production should also be first in sugar production. Due to climatic suitability in southern India, Maharashtra sometimes surpasses Uttar Pradesh in sugar production even though it produces less sugarcane than UP. In 2020-21 where Uttar Pradesh stood first in both sugarcane production and sugar production; On the other hand, in 2021-22, Uttar Pradesh remains at the first place in sugarcane production, but has slipped to the second place in sugar production and Maharashtra has come to the first place.
Sugar Production ( in Lakh Tonnes ) | |||
| Year | Maharashtra | UP | All-India |
| 2020-21 | 106.30 | 110.59 | 311.20 |
| 2021-22 ( projected ) | 138.00 | 104.00 | 355.50 |
Cotton ( Gossypium sop. )
The cultivation of cotton began in the Indian sub-continent, evidence of which comes from the Neolithic sites of Mehrgarh and the Harappan civilization. It is also called white gold.
The following conditions are favourable for cotton production – high temperature, light rainfall or irrigation, frost-free weather, and bright sunlight. 60 to 85 cm annual rainfall is suitable for this. It gives good production in black soil.
In the Ganga-Yamuna Doab, Ruhelkhand and Bundelkhand regions of Uttar Pradesh, cotton is cultivated with the help of irrigation. Here more short fiber cotton and less long fiber cotton is grown.
Cotton is grown in Saharanpur, Muzaffarnagar, Meerut, Hathras, Ghaziabad, Bulandshahr, Aligarh, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Kanpur, Rampur, Bareilly, Moradabad, Mathura, Mainpuri and Farrukhabad.
The following varieties of cotton are grown in the state – U.P. Desi, Bengal cotton, Dholera and Punjab American varieties.
Its cultivation is mainly done along with fenugreek, moong, berseem, rapeseed, clover etc.
It is sown in June-July and cotton is picked from the plants till October-November.
Intensive cotton development program is being run in Agra, Mathura, Aligarh and Hathras.
- Cotton : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 13.01 ( 100 % ) | 35.38 ( 100 % ) | 462 | 45.1 % |
| UP | – | – | – | – |
| Top states | 1. Maharashtra 2. Gujarat 3. Telangana | 1. Maharashtra 3. Gujarat 3. Telangana | 1. Rajasthan 2. Gujarat 3. MP | 1. Rajasthan 2. Haryana 3. MP |
Jute ( Corchorus olitorius )
Jute is grown in the terai region of the state and in the Doab of Saryu and Ghaghra rivers. Bahraich, Maharajganj, Deoria, Gonda, Sitapur and Lakhimpur Kheri are the main jute producing districts. Jute crop is sown in the state in the month of June-July and harvested in September-October. In most parts indigenous variety of jute is sown, which is used for making rope.
- Jute & Mesta : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2020-21 4th advance estimate except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : million hectares
Production : million tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 0.66 ( 100 % ) | 9.56 ( 100 % ) | 2595 | – |
| UP | – | – | – | – |
| Top states | 1. West Bengal 2. Assam 3. Bihar | 1. West Bengal 2. Bihar 3. Assam | 1. Bihar 2. West Bengal 3. Assam |
Tobacco ( Nicotiana tobacum )
In Uttar Pradesh, tobacco is grown in the districts of Varanasi, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Bulandshahr, Mainpuri, Saharanpur and Farrukhabad. Tobacco is cultivated in the state especially for eating and drinking hookah.
- Tobacco : area, production, yield & irrigation
- Data for 2019-20 except irrigation
- Irrigation data for 2018-19 provisional
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Area : ‘000’ hectares
Production : ‘000’ tonnes
Yield : kg / hectare
| Area ( % to all India ) | Production ( % to all India ) | Yield | Area under Irrigation % ( 2018-19 ) | |
| India | 404.29 ( 100 % ) | 801.42 ( 100 % ) | 1982 | 67.9 % |
| UP | 35.00 ( 8.66 % ) | 98.00 ( 12.23 % ) | 2800 | 99.8 % |
| Top states | 1. Gujarat 2. Karnataka 3. Andhra Pradesh 4. UP | 1. Gujarat 2. Andhra Pradesh 3. UP | 1. UP 2. Gujarat 3. Andhra Pradesh | 1. Gujarat 2. UP 3. Bihar |
Therefore, it is clear from this table that :
- Uttar Pradesh is fourth position in Area under Tobacco cultivation.
- UP ranks third in Sugarcane production.
- UP ranks first in Tobacco productivity.
- UP ranks second in area under Irrigation of Tobacco crop.
Opium ( Papaver somniferum )
Barabanki is the largest producer of opium in the state. Apart from Barabanki, opium is also cultivated in Ghazipur. Ghazipur has the only opium factory in the state.
Yield of Major Crops
- Data for 2020-21 ( 4th Advance Estimates )
- Source : Agricultural statistics at a glance – 2021
Yield : kg / hectare
| Crops | India | UP | Max. Yield/State |
| Rice | 2713 | 2759 | 4366 / Punjab |
| Wheat | 3464 | 3604 | 4862 / Punjab |
| Maize | 3195 | 2331 | 6820 / Tamil Nadu |
| Barley | 2805 | ||
| Nutri/ Coarse Cereals | 2146 | 2266 | 6563 / West Bengal |
| Jowar | 1128 | 1578 | 3070 / Andhra Pradesh |
| Bajra | 1436 | 2221 | 2372 / Haryana |
| Ragi | 1771 | ||
| Total Pulses | 892 | 1079 | 1275 / Gujarat |
| Gram | 1217 | 1376 | 1568 / Gujarat |
| Tur | 892 | 988 | 1138 / Jharkhand |
| Urad | 557 | ||
| Moong | 599 | ||
| Lentil | 1001 | 988 | 1139 / MP |
| Foodgrains | 2386 | 2926 | 4606 / Punjab |
| Nine Oilseeds | 1254 | 1054 | 2073 / Tamil Nadu |
| Groundnut | 1676 | 1209 | 2310 / Tamil Nadu |
| Rapeseed & Mustard | 1511 | 1412 | 2027 / Haryana |
| Linseed | 644 | 688 | |
| Sunflower | 1023 | 1382 | 2714 / Telangana |
| Soyabean | 1007 | 687 | 1503 / Telangana |
| Cotton | 462 | 675 / Rajasthan | |
| Jute & Mesta | 2595 | 3172 / Bihar | |
| Sugarcane | 82205 | 81500 | 102730 / Tamil Nadu |
| Tobacco | 1982 | 2800 | 2800 / UP |
Horticulture
Horticulture is a branch of agriculture relating to the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, ornamental plants, flowers and garden crops. It is a capital and labour intensive agriculture. Horticulture may be classified into a number of general divisions as follows :
- Olericulture : vegetable
- Pomology : fruit
- Floriculture : flower
- Arboriculture : aesthetic or ornamental tree
- Landscape gardening and design
- Processing & manufacturing
- Nursery business
- Seed trade
- Storage & marketing
Horticulture and Food Processing Department was established in 1974 in view of immense possibilities of industrial development in the state.
Industrial experiment and training centres have been set up by this department in Basti, Saharanpur, Lucknow, Prayag and Jhansi keeping in view the different agro-climatic conditions of the state. Lucknow centre is for mango and Prayagraj for guava. While the rest are for many fruits. For e.g.
- Horticulture Experiment & Training Centre Distt. Basti.
- Beetle Experiment & Training Centre Distt. Mahoba.
Scheme : Scheme to promote the horticulture by developing fruit belts.
Duration : 5 year ( 2017 to 2021-22 )
About scheme : State government has declared fruit belt for development of three fruit i.e. Mango, Guava and Gooseberry.
Mango fruit belt is covered by 31 Development Blocks of Saharanpur, Meerut, Baghpat, Bulandshahr, Amroha, Pratapgarh, Varanasi, Lucknow, Unnao, Sitapur, Hardoi, Faizabad and Barabanki districts.
For Guava fruit belt, 6 development blocks of district Koushambi and Badaun have been selected and
2 development blocks of district Pratapgarh are selected for Gooseberry fruit belt.
The National Horticulture Mission operated by the Centre since 2005-06 is being operated in the name of Integrated Horticulture Development Mission from 2014-15. Under this mission, at present, programs are being run in 45 districts of the state for expansion of area and production of fruits, vegetables, flowers, spices and medicinal crops.
The ‘National Mission on Micro Irrigation‘ is run by the Central Government for well-planned irrigation of horticultural crops in almost all the districts of the state. Under this, drip and sprinkler irrigation systems are installed.
Under the National Horticulture Mission, the government gives a maximum grant of 50 percent for the establishment of ideal nursery, small nursery, plant health clinic, pack house, pre-cooling unit, cold storage, container, reefer van, ripening chamber, etc.
There is one state level (State Fruit Preservation and Canning Institute, Lucknow) and 10 divisional level educational institutions to promote processing of agricultural/horticultural products in the state. Where diploma degree is given.
The country’s first horticulture call centre has been opened at Rehman Khera, Lucknow-based Central Institute of Subtropical Horticulture.
- Horticulture crop Category wise 2020-21 ( Final Estimate )
- Area : in ‘000’ hectare
- Production : in ‘000’ M
| Area | Production | |||
| 1. Total Horticulture | ||||
| India | 27476.10 | 334602.71 | ||
| UP | 2373.90 ( 8.64 % ) | 40813.85 ( 12.2 % ) | ||
| State ranking | 1. Karnataka2. UP | |||
3. MP1.UP2. West Bengal
3. MP
2. Fruits
India6929.73102481.17UP504.15 ( 7.3 % )11231.46 ( 10.96 % )State ranking1. Maharashtra2. Andhra Pradesh
3. UP1. Andhra Pradesh2. Maharashtra
3. UP
3. Vegetables
India10859.42200445.23UP1307.22 ( 12.04 % )29160.91 ( 14.55 % )State ranking1. West Bengal2. UP
3. MP1. West Bengal2. UP
3. MP
4. Plantation
India4254.7916628.93UP——State ranking1. Karnataka2. Kerala
Tamil Nadu1. Kerala2. Karnataka
Tamil Nadu
5. Aromatic & medicine
India653.20824.99UP135.04 ( 20 % )13.53 ( 1.64 % )State ranking1. Rajasthan2. UP
3. MP1. Tamil Nadu2. Rajasthan
3. MP
6. Flowers
LooseCutTotalIndia322.022151.96828.092980.05UP22.58 ( 7.02 % )49.2669.22118.48 ( 3.98 % )State ranking1. Kerala2. Tamil Nadu
3. Karnataka1. Tamil Nadu2. MP
3. Karnataka1. West Bengal2. Karnataka
3. Chhattisgarh
7. Spices
India4456.9411117.34UP404.92 ( 9.08 % )266.97 ( 2.4 % )State ranking1. Rajasthan2. Gujarat
3. MP1. MP2. Rajasthan
3. Gujarat
8. Honey
India—125.01UP—22.50 ( 18 % )State ranking—1. UP2. West Bengal
3. Punjab
Fruit Production
Fruits like mango, guava, banana, amla ( Indian gooseberry), litchi, jujube, papaya, lemon, watermelon etc. are produced in Uttar Pradesh. The major fruits and their production areas are as follows-
Mango ( Mangifera Indica )
Mango is tropical as well as semi-tropical fruit. Mangoes grow best in temperature around 27 °C. Mango is called the king of fruits. Mango cultivation started in the Indian sub-continent.
Mango is mainly cultivated in the central and western districts of Uttar Pradesh. The main mango producing districts of the state are: Lucknow, Sitapur, Unnao, Barabanki, Ayodhya, Bareilly, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Kanpur, Bulandshahr, Moradabad, Saharanpur, Hardoi, Varanasi etc.
The main varieties of mangoes produced in the state are : Dushehri, Langra, Rataul, Chausa, Lucknow Safeda, Malihabad Safeda, Husnara, Gulabkhas, Surkha, Matiyari and Surkha Jhakharbagh, Bombay Green etc.
Malihabadi Dushehri, Langda and Bombay Green of Lucknow, Safeda and Chausa of Saharanpur, Rataul of Meerut-Baghpat and Langda, Ramkheda and Chausa of Varanasi are famous. Dussehri mangoes are also exported.
The mangoes produced in the state are promoted under the name ‘Nawab Brand‘ in different cities of the country.
Uttar Pradesh ranks first in mango production with share of 23.58 % and the highest productivity in 2021-22. India ranks first in the production of mango at the global level.
- Mango : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 2316.81 | 20385.99 |
| UP | 279.25 ( 12.05 % ) | 4806.65 ( 23.58 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. UP |
3. Odisha1. UP2. Andhra Pradesh
3. Karnataka
| Geographical Indication ( GI – tag ) |
- Allahabad Surkha Guava – 2008 ( up to 2026 )
- Geographical area – UP
- Malihabadi Dusseheri Mango – 2009 ( up to 2028 )
- Geographical Area – UP
- Rataul Mango – 2021
- Geographical Area – UP
- Kalanamak Rice – 2013 ( up to 2030 )
- Geographical Area – UP
- Basmati – 2016 ( up to 2028 )
- Geographical Area – western part of UP, Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, Uttarakhand, J&K
- Mahoba Desawari Pan – 2021 ( up to 2023 )
- Geographical Area – UP
Guava ( Psidium gujava L. )
Guava is a tropical and sub-tropical fruit.
Guava is mainly produced in Prayagraj, Kaushambi, Badaun, Kanpur, Bareilly and Ayodhya districts in the state.
Its main varieties are Safeda, Hafji Lucknow, Karela, Allahabad (Prayagraj) Safeda, Dhaulka Lucknow etc.
Allahabadi Safeda, Lucknow-49 (Sardar) and Lalit Surkha are the exporting varieties.
India ranks first in the production of guava at the global level and Uttar Pradesh occupies the first place in the country with 21.78% share ( 2020-21 ).
- Guava : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 308.09 | 4582.30 |
| UP | 52.22 ( 16.95 % ) | 983.06 ( 21.45 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. UP2. MP3. Bihar | 1. UP2. MP3. Bihar |
Amla/Indian Gooseberry ( Emblica officinalis )
Gooseberry or Indian Gooseberry or Amla or Aonla is an indigenous tropical and sub-tropical plants to the Indian sub-continent. Due to its nutritional and medicinal value, it has become famous for its commercial demand. It is a hardy plant which can be grown in waste lands. The best thing about this tree is that it can survive in extreme hot and cold climatic conditions as well.
In Uttar Pradesh, gooseberry cultivation is done especially in Pratapgarh and in general in many districts.
Uttar Pradesh is the largest producer of Amla in the country. Globally, India ranks first in Amla production.
- Amla : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 100.48 | 1196.84 |
| UP | 36.70 ( 36.52 % ) | 402.63 ( 33.64 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. UP2. MP3. Tamil Nadu | 1. UP2. MP3. Tamil Nadu |
Banana ( Musa paradisiaca)
Banana is a tropical plant, requiring a warm humid climate.
Banana is produced on a large scale in Varanasi, Kaushambi, Prayagraj and Gorakhpur in Uttar Pradesh. Malbhog, Chini-Champa, Alfan, Adheshwar, Dudhsagar and vegetable varieties of bananas are produced here.
India ranks first in the production of bananas in the world. Uttar Pradesh ranks 6th in banana production in the country with a share of 10.45% ( 2021-22 ). [ Andhra Pradesh – First ]
- Banana : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 924.14 | 33061.79 |
| UP | 73.78 ( 7.98 % ) | 3387.51 ( 10.25 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Karnataka2. Kerala3. Tamil Nadu | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. Maharashtra3. Gujarat |
Peach ( Prunus presica )
Peach ( Shaftaloo ) is produced in the western districts of the state and in Lucknow.
- Peach : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 18.34 | 111.23 |
| UP | — | — |
| State ranking | 1. Uttarakhand2. Himachal Pradesh3. J & K | 1. Uttarakhand2. Punjab3. Himachal Pradesh |
Litchi ( Litchi chinensis )
Litchi is produced in Saharanpur, Shamli, Muzaffarnagar and Meerut districts of Uttar Pradesh.
- Litchi : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 97.91 | 720.12 |
| UP | 4.46 ( 4.56 % ) | 38.83 ( 5.39 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Bihar2. Uttarakhand3. West Bengal | 1. Bihar2. West Bengal3. Jharkhand |
Malta
Malta is produced in Saharanpur, Meerut, Varanasi districts of Uttar Pradesh. Its main varieties are mousambi, blood red etc.
- Sweet Orange ( Malta, Mosambi ) : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 216.53 | 3987.91 |
| UP | — | — |
| State ranking | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. Maharashtra3. Telangana | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. Maharashtra3. Telangana |
Lemon ( Citrus lemon )
In the Bundelkhand region of Uttar Pradesh, lemon is produced especially around and in general in all areas.
- Lime / Lemon : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 327.28 | 3548.35 |
| UP | — | — |
| State ranking | 1. Gujarat2. Andhra Pradesh3. Maharashtra | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. Gujarat3. MP |
Orange
Orange is cultivated around Saharanpur and in some areas of Bundelkhand.
- Mandarin ( M. orange, Kinnow, Orange ) : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 476.51 | 6219.38 |
| UP | — | — |
| State ranking | 1. MP2. Maharashtra3. Punjab | 1. MP2. Punjab3. Maharashtra |
Papaya
Papaya is cultivated in Saharanpur, Unnao, Lucknow, Ayodhya etc. districts of Uttar Pradesh.
- Papaya : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 145.88 | 5539.81 |
| UP | 2.30 ( 1.6 % ) | 111.03 ( 2 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Gujarat2. Andhra Pradesh3. Maharashtra | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. Gujarat3. MP |
Watermelon
Watermelon is a kharif crop which is cultivated in the valleys of rivers like Ganga, Saryu Gomti etc.
- Watermelon : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 119.03 | 3254.21 |
| UP | 15.42 ( 12.95 % ) | 696.89 ( 21.4 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Andhra Pradesh2. UP3. Odisha | 1. UP2. Andhra Pradesh3. Karnataka |
Vegetable and Spice Production
Potato ( Solanum tuberosum)
The potato has a wide range of seasonal adaptability. It is a cool season crop and is moderately tolerant to frost. The young plants grow best at a temperature of 24°C. Later growth is favoured at a temperature of 18°C. Tuber production is maximum at 20°C and decreases with the rise in temperature. At about 30°C the tuber production stops totally. Short days are beneficial for tuber production. It can be cultivated up to an elevation of 2300 m. It can be grown as a summer crop in the hills and as winter crop in plains.
India is second only to China in potato production globally, while Uttar Pradesh is the leader in potato production in the country.
- Potato : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 2203.03 | 56172.54 |
| UP | 620.44 ( 28.16 % ) | 15811.31 ( 28.15 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. UP2. West Bengal3. Bihar | 1. UP2. West Bengal3. Bihar |
Although potatoes are cultivated in the entire state, but its main production areas include the districts of Farrukhabad, Kannauj, Hathras, Agra, Meerut, Badayun, Baghpat, Firozabad, Rampur, Aligarh, Ghaziabad, Etawah etc.
Breeder potato seeds obtained from the Central Potato Research Institute, Shimla, are distributed in the entire state after being promoted by 19 State Potato Seed Promotion Areas of the state.
At present, there are more than one thousand cold storages in the state, whose total storage capacity is about 65 percent of the total potato production of the state.
A ‘Potato Research Centre’ Babugarh has been established in Ghaziabad for research on potatoes and other vegetables.
Out of the three agricultural exporting regions of the state – Lucknow, Saharanpur, Agra; Agra is established for potatoes. Potatoes are sold under the brand name ‘Taj’.
- There are three agricultural export zones in the state: Lucknow – Mango, Saharanpur – Mango, Agra – Potato. Apart from this, Uttar Pradesh is also an agricultural export sector for Basmati rice.
Turmeric ( Curcuma longa )
Turmeric is used as spice, dye, and in cosmetic industry and religious ceremonies.
It is an erect, perennial herb grown as an annual crop.
Turmeric prefers a warm, humid, climate with a rainfall of 150 cm and temperature 20°- 30°C. It thrives well up to 1200 m above the mean sea level. Well-drained sandy or clayey loam or red loamy soils having acidic to slightly alkaline pH are ideal for its cultivation.
Although turmeric is cultivated in many districts, but especially in the Bundelkhand region.
- Turmeric : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 292.88 | 1123.86 |
| UP | 1.68 ( 0.6 % ) | 2.36 ( 0.21 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Maharashtra2. Telangana3. Andhra Pradesh | 1. Telangana2. Maharashtra3. Karnataka |
Ginger ( Zingiber officinale )
Ginger is an indigenous plant. India is the largest grower of ginger in the world. Ginger grow well in the warm and humid climate.
Ginger is mainly cultivated in the Bundelkhand districts of Uttar Pradesh.
- Ginger : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 204.84 | 2224.84 |
| UP | 0.91 ( 0.44 % ) | 4.30 ( 0.19 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. UP2. West Bengal3. Bihar | 1. UP2. West Bengal3. Bihar |
Onion ( Allium cepa )
Generally, onion is produced for domestic use in most parts of the state, but it is cultivated on a large scale in the districts of Farrukhabad, Badaun, Mainpuri, Etawah, Kannauj, Etah, Firozabad etc.
- Onion : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 1624.29 | 26641.00 |
| UP | 28.55 ( 1.76 % ) | 470.84 ( 1.77 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Maharashtra2. Karnataka3. MP | 1. Maharashtra2. MP3. Karnataka |
Garlic ( Allium sativum )
Generally, garlic is produced for domestic use in most parts of the state, but it is cultivated on a large scale in the districts of Farrukhabad, Badaun, Mainpuri, Etawah, Kannauj, Etah, Firozabad etc.
- Garlic : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 392.15 | 3189.78 |
| UP | 34.90 ( 8.9 % ) | 207.14 ( 6.5 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. MP2. Rajasthan3. UP | 1. MP2. Rajasthan3. UP |
Coriander & Fennel
- Coriander – Coriandrum sativum
- Fennel – Foeniculum vulgare
Coriander and fennel are mainly cultivated in the districts of Deoria, Kushinagar, Gorakhpur, Azamgarh, Mau, Jaunpur, Sultanpur, Ayodhya, Ambedkarnagar etc.
- Coriander : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 656.46 | 891.32 |
| UP | 6.76 ( 1.03 % ) | 5.31 ( 0.6 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. MP2. Gujarat3. Rajasthan | 1. MP2. Gujarat3. Rajasthan |
- Fennel : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 82.77 | 137.39 |
| UP | 0.72 ( 0.87 % ) | 0.78 ( 0.57 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. Gujarat2. Rajasthan3. MP | 1. Gujarat2. Rajasthan3. MP |
Mushroom ( Agaricus bisporus)
Mushroom is a fungus in which the protein is found abundant. It can be easily grown on paddy straw and wheat straw etc. without soil. Keeping in view the demand, special emphasis is being laid on its cultivation in Uttar Pradesh.
- Mushroom : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | — | 242.87 |
| UP | — | 14.00 ( 5.76 % ) |
| State ranking | — | 1. Odisha2. Maharashtra3. Bihar |
Floriculture
Flowers are cultivated in Varanasi, Kannauj, Mirzapur, Jaunpur, Prayagraj, Lucknow etc. districts of Uttar Pradesh.
Many types of grants are given by the government for nursery of flowers. Lucknow is one of the nine model flower production centres established in India.
Perfume is made from flowers in Kannauj.
India: Uttar Pradesh government to promote flower farming. The Uttar Pradesh government has agreed to join hands with the CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (NERI) to prepare a roadmap for the promotion of flower farming in the state under the National Floriculture Mission launched by the Centre on March 4, 2021; said people who are aware of the development. A decision in this regard, according to them, was taken in a meeting chaired by chief secretary Durga Shankar Mishra, a CSIR-NBRI director, where SK Barik made a presentation on the need and scope for the promotion of floriculture in UP. The NBRI director sought the state government’s support in its endeavours. The CSIR-NBRI is the nodal body appointed by the Centre for the promotion of flower farming across the country. We, in association with the NBRI, will soon prepare a detailed project report (DPR) for the promotion of floriculture in the state and provide all the support the NBRI expects from us horticulture department director RK Tomar said when contacted. He said currently the state government had no separate scheme for floriculture promotion. |
Pharmaceutical and Perfumery
Various facilities are being provided to the farmers by the State Horticulture Department for the cultivation of plants like : Aloe vera (Ghritkumari), Brahmi, Peppermint, Maitha, Tulsi, Safed Musli, Satavari, Sarpagandha, Shankhpushpi, Neem, Ashoka, Arjuna, Bel, Koch, Kalmegh, Ashwagandha, Palmaroja, Lemongrass, Geranium, Khus, Evergreen, Isabgol, Senna etc.
With the aim of preserving and increasing the cultivation of important medicinal crops being grown in the state, gardens are being established under the Herbal Garden Scheme in 18 districts including Gorakhpur, Varanasi, Mathura, Jhansi, Hardoi, Maharajganj, Ballia Gonda etc.
Aloe vera, Amla, Ashwagandha, Brahmi etc. are cultivated on a large scale at private level in Meerut and Saharanpur divisions.
Shivla (Mentha) is a plant similar to mint. Oil (mentha oil) is extracted from the leaves of this plant, from which many medicinal and useful substances are made. It is cultivated in the western districts of Barabanki, Badaun, Rampur, Kannauj, Jalaun, Auraiya, Etawah, Etah etc. of the state. This plant requires more heat and water, so its yield is good in summer.
- Mint / Mentha : Area, Production 2020-21 ( final estimate )
- Area – ‘000’ hectare
- Production – ‘000’ tonnes
| Area | Production | |
| India | 347.28 | 45.80 |
| UP | 346.00 ( 99.63 % ) | 34.71 ( 75.8 % ) |
| State ranking | 1. UP2. MP3. TAMIL NADU | 1. Up2. MP3.Tamil Nadu |
Mentha oil industry is established in the districts of Barabanki, Badaun, Rampur etc. Fragrance and Flavor Development Center has been set up in Kannauj to check mentha oil purity. India accounts for about 85% of the world’s total mentha exports. U.P. contributes to about 90% of the mentha oil production in the country.
Betel Production
Betel ( Paan ) is a perennial vine. Paan is grown on an area of about two and a half thousand hectares in total 24 districts including Mahoba, Banda, Unnao, Rae Bareli, Pratapgarh, Ballia, Ghazipur, Amethi, Mirzapur, Sonbhadra, Lalitpur, Kanpur, Jaunpur, Prayagraj, Lucknow, Varanasi, Sultanpur, Azamgarh.
Mahoba is specially known for betel cultivation in the state. Here in 1981 the Betel Research and Training Centre has been established.
Besides Mahoba, Baraimanpur (Banda) region and Pali region (Lalitpur) are particularly famous for betel cultivation.
Some major betel species : Mahoba Deshwari, Kalkatiya, Kapuri, Bangla, Sagar Bangla, Ayurvedic Bangla, Kaker, Pali Desi Jaiswari Magahi, Sanchi, Banarasi, Sophia, Ramtek, Kapuri Meetha, etc.
From 2012-13, Betel Promotion Scheme is being run in 21 betel producing districts of the state for quality betel production.
Jatropha/Ratanjot ( Jatropha curcas )
Special emphasis is being laid on Jatropha cultivation in the state. The oil obtained from Jatropha seeds is used as a substitute for diesel. Seeds are to be obtained from 4 years after planting of Jatropha. The Jatropha Cloning Garden project is being run in the Bakshi Talab campus ( Lucknow ) under the supervision of Biotech Park ( Lucknow ).
