Introduction
The ‘Animal Husbandry Department’ was established in 1944 by the state government. It strives for the following four dimensions of livestock development: improved animal breeding, animal health, animal management and animal nutrition.
20th livestock Census : Summary
20th Livestock Census Report
Considering the number and past trends over last two decades, there is no livestock species which are on the verge of extinction. However, only Camel and Donkey population is showing declining trends over last four Livestock Censuses i.e., 17th (2003), 18th (2007), 19th (2012) and 20th (2019) Livestock Census. Source : PIB |
Livestock Census & UP
| Category | India | Uttar Pradesh | ||
| In Million | In Million | % Share in County | Position in Country | |
| Cattle | 193.46 | 18.8 | 9.7 | 2nd |
| Buffalo | 109.85 | 33.0 | 30.0 | 1st |
| Sheep | 74.26 | 1.0 | 1.35 | 10th |
| Goat | 148.88 | 14.48 | 9.7 | 3rd |
| Pig | 10.29 | 0.41 | 3.98 | 6th |
| Mithun | 0.30 | |||
| Yak | 0.08 | |||
| Horses & Ponies | 0.34 | 0.076 | 21.11 | 1st |
| Mule | 0.08 | 0.009 | 11.25 | 4th |
| Donkey | 0.12 | 0.016 | 13.33 | 3rd |
| Camel | 0.25 | 0.002 | 0.8 | 4th |
| Poultry | 851.81 | |||
| Total livestock | 512.76 | 67.8 | 13.22 | 1st |
In the 20th Livestock Census of 2019, on comparison with the 19th Livestock Census of 2012:
The following facts emerge at the national level —
- there has been an increase in the population of the following species – Cattle, Buffalo, Sheep, Goat and Pig.
- there has been a decrease in the population of following species – mithun, Yak, Horse & Ponies, Mules, Donkey, Camel.
- the total number of livestock has increased – 4.63%.
On comparison in Uttar Pradesh the following things emerge –
- there has been a decrease in the total livestock (-1.35%);
- there has been an increase in the population of buffalo ( 7.81 % );
- the population of the following animals has decreased – cattle, sheep, goat, pig, Horses & Ponies, Mule, Donkey and Camel.
| Livestock Population — Share of major Species ( 20th livestock census : 2019 ) | ||
| Category | India ( % ) | Uttar Pradesh ( % ) |
| Cattle | 35.94 | 27.77 |
| Buffalo | 20.45 | 48.67 |
| Sheep | 13.87 | 01.47 |
| Goat | 27.80 | 21.35 |
| Pig | 01.69 | 00.6 |
| Others | 00.23 | 00.18 |
In the year 2020-21, there are a total of 2202 veterinary hospitals, 267 ‘D’ category veterinary dispensaries, 2575 animal service centres, 5044 artificial insemination centres and 3 super-frozen semen production centres in the state. Apart from this, Veterinary Polyclinics are working in Gorakhpur, Muzaffarnagar, Lucknow, Baraut (Baghpat) and Saipai (Etawah) for special treatment of animals. One polyclinic each is being made in the remaining division ( mandals ) of the state.
With the contribution of the Central Government, intensive vaccination is done for different diseases from time to time in different districts of the state.
Animal vaccines are produced by the ‘Pashu Jaivik Aushadhi Sansthan’, Lucknow.
The Animal Development Program is basically based on improved breeding. For this, advanced bulls, advanced semen, liquid nitrogen, and artificial insemination centers have been arranged by the state government.
A cattle feed bank ( पशु चारा बैंक ) has been established in Bharari (Jhansi) for the Bundelkhand region with the help of the Centre in the state. Fodder crisis often arises in this area during the summer season.
The Uttar Pradesh Prevention of Cow Slaughter Act, 1955 provides protection to bovine animals from slaughter.
At present there are 8 State Gosadans in the state. UP Goseva Aayog was established in 1999 to promote Gopalan.
A small amount of coarse wool is also produced in the state, which is often used for making blankets. There are 2 government sheep breeding centres in the state for the production of advanced types of sheep.
Pig farming is done in the state for meat. Some quantity of pork is also exported. There are 8 government pig breeding centres for the production of high quality piglets.
According to the All India Medical Council, 182 eggs should be used per person per year, but in the year 2018-19, its annual availability per person in Uttar Pradesh was only 12 eggs. Therefore, efforts are being made to increase their production.
Poultry
Recently, poultry farming has been given the status of agriculture by the state government.
In 2013, the state government has announced the poultry policy for the development of entrepreneurship in the field of poultry farming. In this policy, many types of exemptions are arranged to promote poultry.
With the implementation of Poultry Policy 2013, 1 crore eggs per day coming from other states and 10 crore chicks per year will be produced in the state itself and 263630 additional jobs have been created.
Recently, Uttar Pradesh Poultry Development Policy-2022 has also been announced by the state government.
Uttar Pradesh Poultry Development Policy-2022
- Vision
To Develop animal husbandry as a small scale industry is one of the priorities of the present Government. At present 1.60 crore eggs are being produced daily in the State, while 2.50 crore eggs are consumed daily for which about 90 lakh eggs are being imported from the other States. Similarly, to meet the requirement of broiler meat, about 15 crore day old broiler chicks are imported every year from other States in the State.
The Uttar Pradesh Poultry Development Policy-2022 is being framed with a view to make the State self-reliant and export-oriented by filling the gap in availability relative to demand in poultry products. Under the said policy, in the next five years, it is targeted to set up commercial layer farms with a production capacity of 1crore broiler parent farm for annual 1 crore 72 lakh broiler chicks. This scheme will be helpful in achieving the target of Trillion Dollar Economy of Uttar Pradesh Government and will also create employment opportunities in the primary sector. This policy will be effective for the next five years from the date of its promulgation.
- Purpose
- While ensuring the availability of eggs for protein rich diet for the people in the State, to make the State self sufficient, export oriented in egg production in 5 years.
- To ensure the availability of poultry meat to the public in the state as per the demand, so that the dependence on imports from other states can be reduced.
- To ensure nutritional security.
- To ensure investment of 1500 crore rupees in the next 5 years by developing entrepreneurship in the field of animal husbandry in the state.
- Minimum doubling of income of farmers through poultry farming by generating direct and indirect employment.
- Type of projects
Under the Policy, two types of projects will be allowed to the beneficiaries :
- Establishment of Commercial Layer Farm.
- Establishment of broiler parent farm.
- Other Concessions and Discounts
- Electricity Duty:- 100% rebate on electricity duty will be given for 10 years in the electricity bill of poultry units established under the scheme from the budget of Pashudhan Vibhag.
- Stamp Duty:- 100% exemption on stamp duty will be given on land purchased or taken on lease for the unit establishment under the policy. For this, bank guarantee and certificate of Chief Veterinary Officer will be mandatory.For this Notification Order will be issued by Stamp and Registration department with the consent of Pashudhan Vibhag.
- Eligibility under the Scheme
- The beneficiary of the scheme must be a resident of the State.
- Preference will be given to the beneficiary applying for the first time in the Scheme, but such beneficiaries who have been benefited between March 2013 to March 2017 will be eligible for the scheme, subject to the condition that they have a layer unit of maximum 30,000 birds capacity or a broiler parent farm of 10,000 birds. Under the current policy, only one unit will be allowed to the beneficiary / farmer / entrepreneur and will be included in one project maximum.
- It is mandatory to have 1 acre for 10 thousand commercial layer unit, 2.5 acres for 30 thousand commercial layer unit, 4 acres for 60 thousand commercial layer unit and 4 acres for 10 thousand broiler parent land owned or on lease by the beneficiary.
- Dedicated Portal and Database Management and Project Facilitation Center for Monitoring
- All the activities to be done under the Poultry Development Policy will be conducted through a dedicated portal of the Animal Husbandry Department. All the applications by the beneficiaries of Poultry Development Policy will be done on this portal.
- Training and Capacity Development
- For the establishment of Poultry unit entrepreneurship development management and technical training to the selected beneficiaries will be imparted through reputed institutions of State and National level. Beneficiaries will be made to visit other States as per requirement for information about new techniques of poultry farming.
- Nodal Department
- Animal Husbandry Department
Apiculture ( Beekeeping )
Apiculture is the science and culture of honeybees and their management. Beekeeping (or apiculture, from Latin apis, a bee) is the practice of intentional maintenance of honey bee colonies, commonly in hives, by humans.
A beekeeper (or apiarist) may keep bees in order to collect honey and beeswax, or for the purpose of pollinating crops, or to produce bees for sale to other beekeepers ( apiarists ). A location where bees are kept is called an apiary.
It is a subsidiary cottage industry. Apart from honey, wax, propolis, royal jelly etc. are obtained from this. Bees increase the yield by cross-pollination in horticultural crops. Beekeeping/beekeeping program is being run in 16 districts of the state.
Sericulture in UP and its impact on development of UP
Cow/Buffalo Rearing
Animal husbandry is the second largest occupation in the state after agriculture. There are vast possibilities for the development of bovine ( cow ) and mahishvanshi ( buffalo ) animals in the state. The main objective of the State Animal Breeding Policy is to increase the milk production of Govanshi and Mahishvanshi animals, to produce best bullocks for agricultural works and to conserve the Govanshi / Mahishvanshi species of Indian origin.
Special efforts are being made to control 10 major diseases like rabies, swine fever, tuberculosis, brucellosis, pulloram etc.
The disease called Rinderpest has ended in the state, while a special vaccination campaign is being run to control foot and mouth disease ( खुरपका-मुहपका बीमारी ).
Milk Production
The package programme adopted to increase the production of milk is known as White Revolution in India. The white revolution in India occurred in 1970, when the National Dairy Development Board ( NBRD ) was established to organise the dairy development through the co-operative societies.
Current Data ( 2021-22)
Source : Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics 2022. |
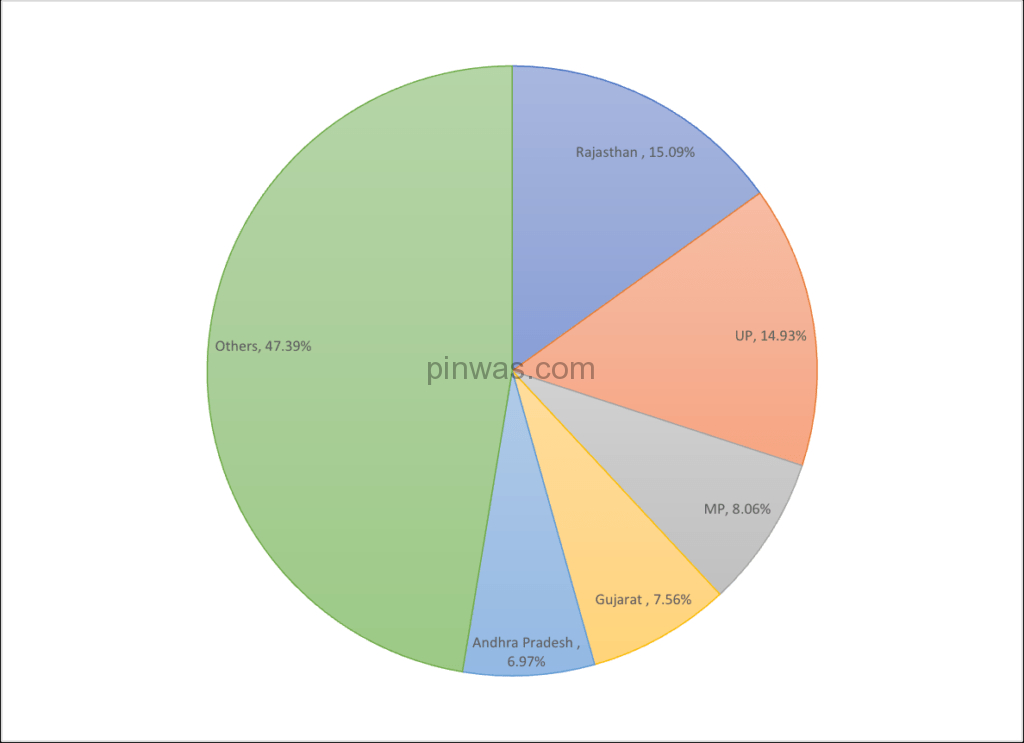
The dairy development programme through co-operative societies was first established in the state of Gujarat. The co-operative societies were most successful in the Anand District of Gujarat.
The increase in milk production has also been termed as Operation Flood.
Prof. Varghese Kurien (1921-2012) is considered as the ‘Father of White Revolution’ in India.
In Uttar Pradesh, Milk Development Department and the ‘Uttar Pradesh Rajya Dugdh Parishad’ were established in 1976 with the objective of providing financial and technical assistance to milk unions, determining areas, determining prices and implementing the Milk Products Regulation Order. ( ? )
Pradeshik Co-operative Dairy Federation, 1962 (PCDF) – It was formed in 1962 for the development of milk and dairy in the state. Operation Flood-1 was conducted under this. The main tasks of this federation include the formation of co-operative milk societies at the village level and through them the overall system of milk procurement, milk collection, processing, milk product manufacturing and distribution etc. i.e. ‘pre-production to post-marketing’.
- Noida Dairy Project (Noida Dairy Project) is under this federation, from where milk is supplied to Delhi.
Uttar Pradesh Rajya Dugdh Parishad – The council was established in 1976 as a regular body under the Uttar Pradesh Milk Act, 1976. The main work of this council is to implement licensing, area reservation, milk pricing and producer regulation orders.
- In addition to this, PCDF Like milk procurement, collection, processing and distribution of milk by forming milk committees at the village level, the work of the council is also included in the activities of the council.
Milk Union ( Dugdh Sangh ) –
- The first regular milk union in Uttar Pradesh and the country was established in Lucknow in 1938. The name of this milk union was – ‘Lucknow Milk Producers Co-operative Union Limited ( लखनऊ दुग्ध उत्पादक सहकारी संघ लि० ).
- At present, total 59 milk unions are functioning in the state.
- Of these, 40 milk unions and one Noida Dairy Project are being run by the Pradeshik Co-operative Dairy Federation (PCDF), which is the sole implementing agency for the implementation of milk development programmes.
- The remaining 19 milk unions are being operated under the State Milk Council ( Rajya Dugdh Parishad ).
Operation Flood-II was started in 1973 in three districts of the state- Varanasi, Meerut and Ballia, under Operation Flood started by the Central Government in 1970-71.
Operation Flood-II (1982-83 to 1987) and Operation Flood-III (1987 to 1996-97) lasted. In this, 30 districts of the state were included. Milk unions were established in the remaining districts.
PCDF has dairy plants in Noida, Prayagraj, Aligarh, Mathura, Lucknow, Gorakhpur, Varanasi, Meerut, Bareilly, Firozabad, Moradabad, Ayodhya, Kannauj and Jhansi.
The biggest milk plant of the state is being set up in Mathura district.
The only cow milk plant in Uttar Pradesh has been established in Kannauj.
Milk Policy-2018 – Uttar Pradesh Government has implemented Milk Policy 2018 to promote processed milk and milk products and to increase per capita milk consumption. The objective of this policy is to provide high quality milk products to the milk consumers. This will also provide self-employment to the farmers of the state in the milk business.
The UP Milk Development and Milk Production Promotion Policy, 2022 –
- Paving the way for investment up to 5,000 crore in dairy sector in the state over the next five year.
- Creation of about 1.25 lakh jobs.
- The plan is to increase the level of milk processing from the current 10% to 25% and increase the marketable surplus of processed milk from 44% to 65%.
- A subsidy of 10% up to a maximum of Rs 5 crore will be given for setting up milk processing plants, or investment in plant, machinery, technical or civil work for the expansion of existing plants. A Rs 10 crore interest subsidy over five years will also be given. For the first time, the government will also give a subsidy of Rs 7.5 crore on setting up a cattle feed factory.
- The policy, the official said, will help in establishing greenfield projects and development of existing capacity. The government will be seeking investments in cattle feed plants, refrigerated vans, insulated milk tanks and other cold chain investments.
Integrated Dairy Development Project – This is a 100% Centrally Sponsored (Non Operation Flood) project. Its objective is to create milk production, procurement, marketing and employment in the backward areas of the state.
Nand Baba Puraskar Yojana – This scheme is being run with the aim of promoting animal husbandry in the state and creating competition among milk producers. Under this scheme, the three producers who supply the maximum amount of indigenous breed cow’s milk to the Milk Union are given one lakh at the state level and Rs. 51 thousand at the district level, shield and certificate.
To promote milk production, Rs 61 crore will be spent on the Nand Baba Milk Mission scheme in the financial year 2022-23.
Gokul Puraskar Yojana – In this scheme, milk producers under the cooperative sector to compete among themselves and to motivate them to keep good quality milch animals, one milk producer from each milk union of the state, who is the most milk producer, who will be selected for milk development. Those who are members of the Cooperative Milk Producers’ Society formed under the Milk Production Cooperative Union working under the department and selling milk to the milk union, are rewarded with this award. In this, the first, second and third place holders are given an amount of Rs 1.50 lakh, Rs 1 lakh and Rs 50 thousand respectively.
Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay Dairy Project – This scheme is being run by the Yogi government in place of Kamdhenu Dairy Scheme. Its objective is to increase milk production from small units as well as provide employment opportunities at the local level.
