Introduction
Government income from all sources is termed public income or public revenue, which can be categorised into two types :
- Source of Public Revenue
- Tax Revenue
- Non-Tax Revenue
Tax
Meaning –
Tax is a mandatory payment made by citizens to fund public spending. It’s legally enforced, and refusal to pay is not permitted.
Definition –
“A Tax is a compulsory payment made by a person or a firm to a government without reference to any benefit the payer may derive from the government.” – Anatol Murad
Characteristics of Tax –
- A tax is an obligatory payment to the government. Those subject to a tax must fulfill this obligation, and failure to do so is punishable.
- No direct benefits are guaranteed in return for paying taxes.
- Every tax requires a sacrifice from the taxpayer.
- It is important to note that taxes are not imposed as fines or penalties for legal violations.
Some of the tax revenue sources are :-
- Income tax
- Corporate tax
- Sales tax
- Surcharge and
- Cess
Types of Tax :
- Direct Tax
- Indirect Tax
Direct Tax :
A direct tax is one that’s imposed on a person’s income and wealth, paid directly to the government. The burden of this tax can’t be shifted to others. It’s progressive, meaning it’s based on a person’s paying capacity, collecting more from the wealthy and less from the poor. An example is Income Tax.
Indirect Tax :
Indirect Tax is a tax applied to those who buy goods and services, paid indirectly to the government. The tax burden can be shifted to another person. It’s levied equally on all, regardless of wealth, e.g., excise duty, sales tax, custom duty, entertainment tax, service tax, etc.
Tax Reforms in Uttar Pradesh
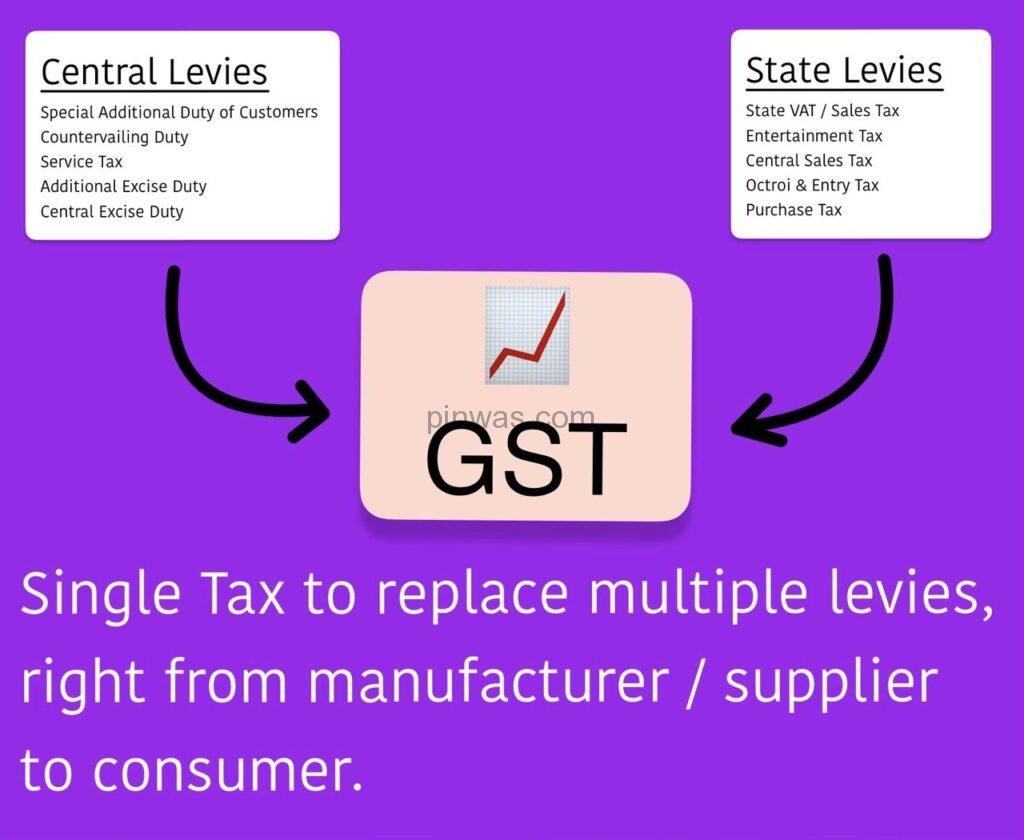
GST Implementation (2017) : Replaced multiple complex taxes with a unified system, reducing compliance costs and simplifying business operations.
Stamp Duty Reduction (2018) : Reduced stamp duty on property registration from 7% to 6%, making property acquisition more accessible and affordable.
Simplified Tax Structure : Minimised the number of taxes and levies on businesses, lowering the overall cost of doing business.
Online Tax Filing and Payment : Enabled easier online tax filing and payment, reducing time and cost of tax compliance.
GST ( Good & Service Tax )
Destination based : Consider goods manufactured in Uttar Pradesh and are sold to the final consumer in Nagaland. Since Goods & Service Tax is levied at the point of consumption, in this case, Nagaland, the entire tax revenue will go to Nagaland and not Uttar Pradesh. Components of GST : The component of GST are of 3 types. They are: CGST, SGST & IGST.
Advantage of GST :
|
Description of some taxes in Uttar Pradesh
Commercial Tax
Sales Tax is the largest source of revenue for the state government. Following that, the subsequent sources of revenue include State Excise Duty and Stamp and Registration Fees.
Before independence, the Sales Tax Act was enacted in 1939. After independence, in 1948, a new law called the Uttar Pradesh Sales Tax Act 1948 was introduced. In 1994, it was renamed as the U.P. Trade Tax Act 1994.
In 1999, the state government passed a new law called the Uttar Pradesh Entry Tax Act 1999.
In the state, from January 1, 2008, the Value Added Tax (VAT) system was implemented in place of the Sales Tax at 15 rates, where only 4 rates were specified.
From July 1, 2017, in the state, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been implemented as a unified tax on the supply of goods and services.
Despite the implementation of the GST system in the state, several items such as petrol, diesel, alcohol, natural gas, etc., are still subject to the previous VAT taxation system.
Stamp and Registration Fees
After trade tax and excise duty, stamp and registration fees are the main source of state tax revenue.
The Stamp and Registration Department is an extremely important department that interacts directly with the public and provides them with services.
The task of registering various types of documents, such as deeds of sales, wills, etc., involved in transactions among parties and ensuring their safekeeping indefinitely, is carried out by the Registration Department.
Excise Duty
As per Article 47 (Prohibition) of the Constitution, the fundamental policy of the state government’s Excise Department is the development, regulation, and effective control of the prohibition of intoxicating substances. Accordingly, prioritizing the prohibition policy, the Excise Department ensures that maximum revenue is generated through the legal sale of intoxicating substances, with proper supervision and control.
Excise duty (on alcohol, bhang, marijuana, and beer) is a significant source of revenue for the state government. The Excise Department spends only one percent of its income on its expenses; the remaining 99 percent is utilised for the state’s development projects.
In the state, a new system replaced the liquor business monopoly/syndicate system from 2001-02, allocating licenses to small businesses through a lottery system.
Sugar syrup (molasses) is obtained as an additional byproduct from sugarcane. Uttar Pradesh is a leading state in sugar production. Apart from alcohol manufacturing, sugar is also used in the production of chemicals such as acetic acid, citric acid, yeast, animal and poultry feed, charcoal briquettes, and more.
In the state, 60 to 76 percent of the total alcohol produced is used in the production of other goods or is exported domestically or internationally.
Ethanol Blending Initiative in Uttar Pradesh :
- Pilot Project Inception : The Indian government launched a pilot project in Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra in 2001-02.
- Gasohol Production : The project aimed to produce gasohol from power alcohol.
- Initiation of Ethanol Blending : Starting in 2008, the scheme involved blending 5% power alcohol (ethanol) with petrol at most of the state’s oil terminals and depots.
- Increased Ethanol Blend : However, since January 2013, the blending rate was increased to 10% ethanol with petrol.
- Uttar Pradesh’s Contribution : Uttar Pradesh plays a significant role, contributing approximately 40% to the country’s total ethanol production.
Prohibition Around Pilgrimage Sites in the State :
- Scope of Prohibition : A comprehensive alcohol ban is in effect within a one-kilometre radius of 19 pilgrimage sites in the state.
- Included Sites : These sites include notable places like Vrindavan, Ayodhya, Naimisharanya, Peeraan Kaliyar, Deva Sharif, Devband, Jain pilgrimage sites, Krishna Janmasthan, Triveni Sangam, Kashi Vishwanath, and more.
- Special Consideration : Meat prohibition is also enforced at Jain pilgrimage sites.
Shop Closures on Special Occasions :
- Independence Day : August 15
- Republic Day : January 26
- Dr. Ambedkar’s Birthday : April 14
- Mahatma Gandhi’s Birthday : October 2
- Additional Days : Three more days as determined by the District Magistrate’s discretion
Alcohol Sales Prohibition in Specific Areas :
- Gandhi Villages : Prohibition on alcohol sales near Gandhi villages.
- Dalit and Slum Areas : Prohibition on alcohol sales in these areas.
- Ambedkar Villages : Alcohol sales are restricted in the vicinity of Ambedkar villages.
Uttar Pradesh is a state abundant in molasses and alcohol. Therefore, the department’s endeavour is to establish as many alcohol and molasses-based industries in the state as possible.
Entertainment Tax
Entertainment Tax is a significant source of state revenue.
Regulatory Framework : The operation of entertainment activities in Uttar Pradesh is governed by the following regulations and rules :
- Uttar Pradesh Cinemas (Regulation) Act 1955 and related rules of 1951
- Uttar Pradesh Amusement and Betting Tax Act 1979 and related rules of 1981
- Video Display (Regulation) Rules 1988
- Cable TV Network (Display) Rules 1997
Administration : These regulations and rules are administered by the Entertainment Department.
After the implementation of the GST system in the state on July 1, 2017, the entertainment tax has been subsumed under GST.
Entertainment Industry in the State :
- 330 single-screen cinemas
- 60 multiplexes
- 200 screens
- 21.62 lakh cable subscribers to cable operators
- 30 lakh subscribers to DTH services
Cinemas in Uttar Pradesh: A State of Transition & related issues :
- Reduced Operational Cinemas : Out of the 1018 cinemas in the state, only 371 remain operational.
- Multiplex Expansion : Multiplexes are expanding rapidly in major cities.
- Challenges in Smaller Towns : However, they face challenges in opening up in smaller towns.
- Lack of Incentives : The primary obstacle is the lack of sufficient incentives for multiplexes to establish themselves in these areas.
Cable TV services have been operating in the state since 1991-92.
Economic Reforms in Uttar Pradesh
One Stop Shop : Establishment for streamlined business setup and approvals, expediting the process for new businesses.
Ease of Doing Business Reforms : Streamlined processes such as obtaining construction permits and property registration, leading to improved rankings in the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business Report.
Infrastructure Development : Investment in new roads, highways, and airports to facilitate business operations and attract investments.
Ambitious Growth Target : Uttar Pradesh aims to become a trillion-dollar economy by 2030, thanks to the confidence in the impact of these reforms.
Agricultural Sector Improvement : Subsidies, crop diversification, farmers’ markets, and research and development investments have increased agricultural productivity and improved farmer incomes.
UP Achieves 2nd Place in 2019 Ease of Doing Business Ranking |
| According to a report released by the Central Department of Industry and Internal Trade on September 5, 2020, Uttar Pradesh secured the second place in the country’s Ease of Doing Business ranking for 2019. In 2018, Uttar Pradesh was ranked 12th. This achievement can be attributed to the significant steps taken by the state government to reform the industrial sector. |
Uttar Pradesh’s Ambitious Budget for 2023-24 & Economic Reforms |
Startups :
Infrastructure :
Metro/RRTS/Expressways :
Agriculture :
Tourism :
Renewable Energy :
Ease of Doing Business :
Future Potential :
|
Impact of Reforms
Economic Growth : Uttar Pradesh consistently outpaces the national GDP growth rate, attracting substantial investments.
Improved Business Environment : Reforms have fostered a favourable environment for businesses, spurring economic activity.
Attractive Investment Destination : The state has elevated its stature as an attractive investment destination, benefiting both businesses and the overall economy. For eg. The UPGIS.