Introduction
Article 202 of the Indian Constitution mandates the presentation of receipt and expenditure estimates of the state government for the financial year (from April 1st to March 31st) before the State Legislature. This is referred to as the “Annual Financial Statement” in the Constitution and is also commonly known as the “budget.”
The Finance Minister of Uttar Pradesh, Mr. Suresh Kumar Khanna, presented the budget for the financial year 2023-24 on February 22, 2023.
Budget : Important Points
Important points of the Budget for 2023-24 are as follows :
Size of the Budget:
The budget for 2023-24 amounts to Rs. 690,242.43 crore, including a new scheme of Rs. 32,721.96 crore.
Total Receipts:
Total receipts estimated for the budget of 2023-24 are Rs. 683,292.74 crore.
Out of this, revenue receipts are estimated at Rs. 570,865.66 crore, and capital receipts are estimated at Rs. 112,427.08 crore.
These receipts are Rs. 107,163.37 crore more than the revised estimate of 2022-23, which was Rs. 576,129.37 crore.
Total Expenditure:
Total expenditure for the budget of 2023-24 is estimated at Rs. 690,242.43 crore.
Out of the total expenditure, revenue account expenditure is Rs. 502,354.01 crore, and capital account expenditure is Rs. 187,888.42 crore.
Revenue Account Expenditure:
In the budget estimate for 2022-23, revenue expenditure was Rs. 456,089.06 crore. For the financial year 2023-24, it is estimated at Rs. 502,354.01 crore.
Thus, in the financial year 2023-24, revenue expenditure is estimated to increase by Rs. 46,264.95 crore.
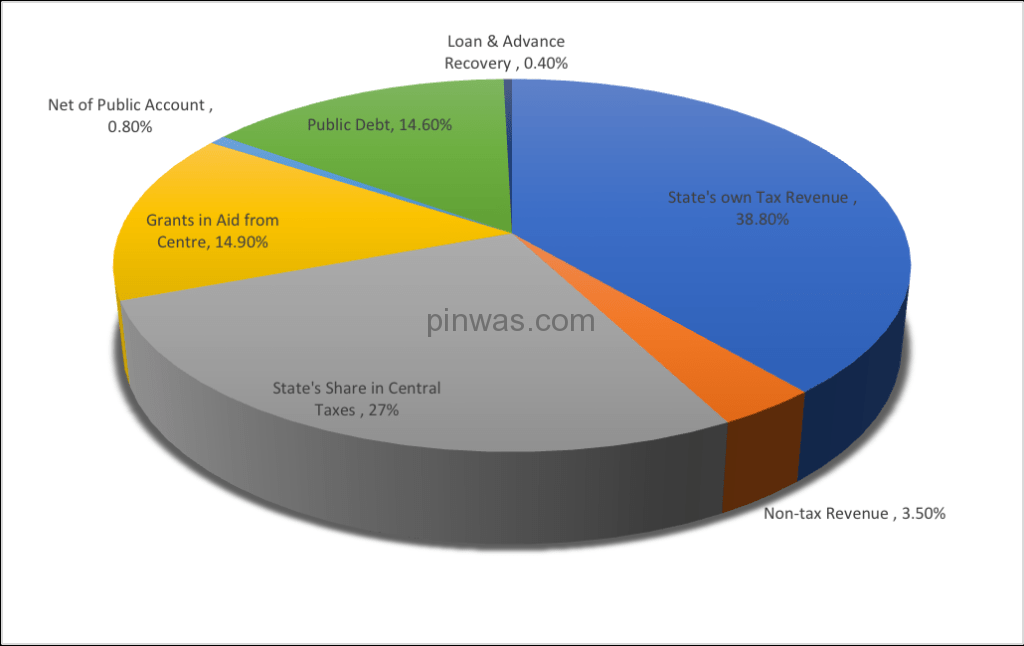
Rupee Comes From :
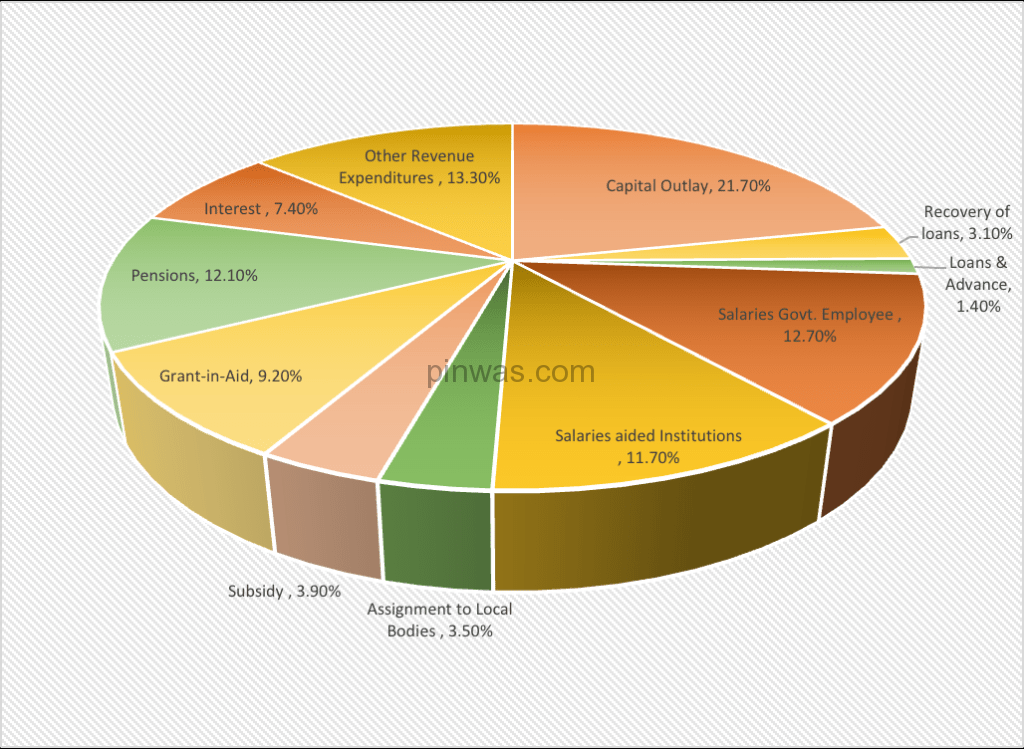
Rupee Goes to :
Sector wise Revenue Expenditure (In ₹ crore) | |||
| Item | Budget Estimate 2022-23 | Budget Estimate 2023-24 | % increase / decrease |
| 1. General Services | 177670.39 | 193465.41 | 8.89 |
| 2. Social Services | 169118.25 | 181579.25 | 7.37 |
| 3. Economic Services | 91300.63 | 103596.27 | 13.47 |
| 4. Assignment to Local Bodies & Panchayat Institution | 180000.02 | 23713.08 | 31.74 |
Main Items of Revenue Account Expenditure (in ₹ crore) | |||
| Item | Budget Estimate 2022-23 | Budget Estimate 2023-24 | % Increase / decrease |
| Interest Payments | 48487.46 | 52755.56 | 8.80 |
| Education, Sports, Art & Culture | 71061.12 | 77455.03 | 9.00 |
| Health & Family Welfare | 33022.25 | 37335.02 | 13.03 |
| Social Welfare & Nutrition | 30194.22 | 31964.98 | 5.86 |
| Agriculture & Allied Activities | 14671.56 | 16406.77 | 11.83 |
| Rural Development | 21176.96 | 23153.10 | 9.33 |
| Energy | 23072.91 | 27215.15 | 17.95 |
| Transportation | 5352.48 | 7118.29 | 32.99 |
Capital Account Expenditure :
In the budget estimate for 2022-23, capital account expenditure was Rs. 159,429.92 crore. In the budget estimate for 2023-24, it is estimated to be Rs. 187,888.42 crore.
Therefore, in the budget for 2023-24, capital expenditure is estimated to increase by Rs. 28,458.51 crore (17.85 per cent).
Within this increase, capital outlay mainly increased by Rs. 23,572.45 crore (19.02 per cent).
The decrease in the internal debt of the State Government is estimated to be Rs. 1,378.23 crore (4.45 per cent).
Receipt from the Central Government :
In the budget estimate for 2023-24, the total receipts from the Central Government in the form of the state’s share in central taxes, grants-in-aid, and loans and advances are estimated to be Rs. 305,379.89 crore.
This represents an increase of Rs. 6,022.24 crore (2.01 per cent) compared to the revised estimate for 2022-23, which is Rs. 299,357.65 crore.
Revenue Account Receipts :
In the budget for 2023-24, the state’s own tax revenue is estimated to increase by Rs. 77,396.02 crore (41.78 per cent) from the revised estimate for 2022-23, which is Rs. 185,237.98 crore.
Major Items of State’s Own Tax Revenue (in ₹ crore) | |||
| Items | Revised Estimate 2022-23 | Budget Estimate 2023-24 | Change in Percent |
| 1. State GST | 76709.80 | 108212.00 | 41.07 |
| 2. Land Revenue | 243.07 | 962.00 | 295.77 |
| 3. Stamp & Registration Fee | 24266.69 | 34560.00 | 42.42 |
| 4. State Excise Duty | 41349.27 | 58000.00 | 40.27 |
| 5. Sale Tax | 31541.50 | 41788.00 | 32.49 |
| 6. Vehicle Tax | 8770.55 | 12672.00 | 44.48 |
| 7. Electricity Tax | 2357.10 | 6440.00 | 173.22 |
| Total | 185237.98 | 262634.00 | 41.78 |
Contingency Fund :
There is no provision for the Contingency Fund (net) in the budget for 2023-24. In the financial year 2022-23, the contingency fund was also estimated to be Rs. 0.00.
Public Account :
For the financial year 2023-24, the net receipts from transactions under the public account are estimated to be Rs. 5,500 crore.
This is Rs. 500 crore less than the budget estimate for 2022-23, which was Rs. 6,000 crore.
Net Result of All the Transaction :
The net result of all transactions in the budget estimates for 2023-24 is Rs. (-) 1,449.69 crore.
The final balance, based on the net result of the initial balance and all transactions, is Rs. 35,957.42.
Revenue Surplus :
In the budget estimate for 2023-24, the revenue surplus is estimated to be Rs. 68,511.65 crore.
In the budget estimate for 2022-23, it was estimated to be Rs. 43,123.65 crore. In the revised estimate for 2022-23, it is estimated to be Rs. 53,907.26 crore.
In 2021-22, the revenue surplus was estimated to be Rs. 23,210.09 crore. In actual data, a revenue surplus of Rs. 33,430.06 crore has been achieved.
Fiscal Deficit :
In the financial year 2023-24, the fiscal deficit is estimated to be Rs. 84,883.16 crore.
This represents 3.48 per cent of the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP).
In the budget estimate for 2022-23, it was Rs. 81,177.98 crore, which increased to Rs. 81,325.63 crore in the revised estimate.
In the actual data for 2021-22, the net fiscal deficit is Rs. 39,286.42 crore.
Capital Outlay :
In the budget for 2023-24, the capital outlay is estimated to be Rs. 147,492.92 crore.
In the budget estimate for 2022-23, it was estimated to be Rs. 123,919.85 crore, which increased in the revised estimate to Rs. 126,601.11 crore.
In 2021-22, Rs. 71,442.55 crore was spent under capital outlay.
Budget at a Glance : The financial year 2023-2024
Comparative details of actual figures for the year 2021-2022, budget estimates for the year 2022-2023, revised estimates, and income-expenditure estimates for the year 2023-2024 are shown in the following table :
Budget at a Glance (In ₹ Crore) | ||||
| Item | 2021-22 Actual | 2022-23 BE | 2022-23 RE | 2023-24 BE |
| 1. Revenue Account Receipts | 37011.44 | 49921.71 | 478816.53 | 570865.66 |
| 2. Tax Revenue * | 307725.79 | 367153.76 | 354983.28 | 445871.59 |
| 3. Non-tax Revenue # | 63285.65 | 132058.95 | 123833.25 | 124994.07 |
| 4. Capital Account Receipt | 76690.62 | 91739.00 | 97312.84 | 112427.08 |
| 5. Recovery of Loans | 939.43 | 2565.00 | 2565.00 | 3312.18 |
| 6. Borrowing & Other Liabilities (out of which ways & means Advances from RBI) | 75751.19 | 89174.00 | 94747.84 | 10911.90 |
| 7. Total Receipts (1+4) | 447702.06 | 590951.71 | 576129.37 | 683292.74 |
| 8. Expenditure on Revenue Account, in which | 337581.38 | 456089.06 | 4,24,909.27 | 502354.01 |
| 9. Interest Payment | 44875.56 | 48487.46 | 47865.50 | 52755.56 |
| 10. Expenditure on Capital Accounts, in which | 102381.85 | 159429.92 | 160363.02 | 187888.42 |
| 11. Capital Outlay | 71442.55 | 123919.85 | 126601.11 | 147617.29 |
| 12. Loan Repayments in which ways & means Advances redemption from RBI | 28725.94 | 32563.29 | 22565.13 | 31181.43 |
| 10000.00 | 10000.00 | 0.00 | 10000.00 | |
| 13. Total Expenditure (8+10) | 439963.23 | 615518.98 | 585272.29 | 690242.43 |
| 14. Revenue Surplus (1-8) | 33430.06 | 43123.65 | 53907.26 | 68511.65 |
| 15. Fiscal Deficit | 39286.42 | 81177.98 | 81325.63 | 84883.16 |
| 16. Primary Deficit (15-9) | -5589.14 | 32690.52 | 33460.13 | 32127.60 |
| * This include state’s own taxes & state’s share in central taxes. # This include state’s own taxes & grants Received from Centre. | ||||
Tax, Debt & Fiscal Restructuring
Gross Tax Collection/Gross State Domestic Product :
Tax collection as a percentage of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) was 16.5 per cent in the actual data for 2021-22, 17.3 per cent in the revised estimate for 2022-23, and 18.3 per cent in the budget estimate for 2023-24.
This indicates a stable improvement in revenue collections in relation to Gross State Domestic Product.
Debt/Gross State Domestic Product :
This ratio was 28.3 per cent in 2013-14, which became 33.14 per cent in 2021-22.
It is 34.2 per cent in the revised estimate for 2022-23 and 32.1 per cent in the budget estimate for 2023-24.
The increase in the debt-to-GSDP ratio is due to the issuance of power bonds of Rs. 29,602.60 crore in 2015-16 and Rs. 14,801.29 crore in 2016-17 under the UDAY Scheme for the financial restructuring of electricity distribution companies.
Indicators as a percentage of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) | ||||||
| Items | 2022-23 BE | 2022-23 RE | 2023-24 BE | For next 3 years | ||
| 2024-25 | 2025-26 | 2027-28 | ||||
| 1. State’s own Tax Revenue | 10.8 | 9.0 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.9 | 11.0 |
| 2. State’s own Non-Tax Revenue | 1.1 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| 3. Revenue Surplus | 2.1 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.5 |
| 4. Fiscal Deficit | 3.96 | 3.97 | 3.48 | 3.24 | 2.95 | 2.80 |
| 5. Total Borrowing & Order Liabilities | 32.5 | 34.2 | 32.1 | 31.7 | 31.0 | 30.2 |
Medium Term Fiscal Restructuring Policy :
The estimated growth rate for GST and VAT in the medium term, in general, is 13 percent for 2024-25 and 14 percent for the following years.
The annual growth rate in non-tax revenue since 2023-24 is estimated to be 6 percent, 7 percent, and 8 percent, respectively.
The state’s share in central taxes has been estimated to be 13 percent in 2024-25 and 14 percent in subsequent years, based on the budget estimate in 2023-24.
Grants-in-aid from the Central Government are expected to grow at 10 percent.
Based on the budget estimate of 2023-24, revenue expenditure is calculated to grow at 11 percent in 2024-25 and 11.5 percent and 12 percent in subsequent years.
Indebtedness of the Government :
In the budget estimate of 2022-23, the government’s indebtedness was calculated to be Rs. 666,153.39 crore.
In the revised estimate, it is Rs. 700,445.52 crore.
For the year 2023-24, it is estimated to increase to Rs. 784,113.65 crore, which is 32.1 percent of GSDP.
Important Announcement in the Budget Speech
The growth rate in Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) for 2023-24 is estimated to be 19 percent.
The state’s share in the country’s GDP is more than 8 percent.
The unemployment rate in the state was 14.4 percent before 2017, but it has currently reduced to 4.2 percent.
The UP Global Investors Summit was organized in Lucknow between 10th and 12th February 2023.
More than 19,000 MoUs worth about Rs. 33.50 lakh were signed at the summit.
Most of the MoUs were signed in renewable energy (16 percent), electronics (12 percent), industrial parks (11 percent), education (9 percent), and logistics (9 percent).
Farmers
The Minimum Support Price (MSP) for wheat in the Rabi season 2022-23 was determined at Rs. 2,015 per quintal.
A total of 3.36 lakh metric tonnes of wheat were purchased from 87,991 farmers in the marketing season, against which Rs. 675 crore was paid.
The Government of India determined the MSP for common grade paddy at Rs. 2,040 per quintal and for Grade-A paddy at Rs. 2,060 per quintal.
A total of 62.66 lakh metric tonnes of paddy have been purchased, against which Rs. 12,000 crore has been paid to 10.30 lakh farmers.
More than Rs. 51,639.68 crore has been transferred through DBT (Direct Benefit Transfer) till now under the Prime Minister Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana in the year 2022-23.
Women and Child Development
Under the ‘Mukhyamantri Kanya Sumangala Yojana,’ every beneficiary is provided with a sum of up to Rs. 15,000.
A proposed budget of Rs. 1,050 crore is allocated for the year 2023-24.
To make rural women self-dependent, women self-help groups are established under the ‘Mahila Samarthya Yojna.’ Rs. 63 crore is proposed for this scheme in 2023-24.
Ninety-five percent of children were vaccinated in the state until October 2022. Under ‘Mission Indra Dhanush,’ more than 3,682,000 children and more than 1,031,000 pregnant mothers were vaccinated.
Under the Uttar Pradesh Rani Laxmibai Mahila Evam Baal Samman Kosh, economic and medical support is provided to women and girls affected by heinous violence. In the financial year 2023-24, Rs. 56 crore was proposed for this initiative.
The Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Scheme is operational in 71 districts.
The Rastriya Poshan Abhiyaan is in operation to reduce malnourishment in children up to 6 years old, decrease anemia in children aged between 6 months and 59 months, and support pregnant women. A budget of Rs. 455.52 crore was proposed for this in the 2023-24 budget.
Youth and Employment
Rs. 3,600 crore has been proposed for the Swami Vivekananda Yuva Sashaktikaran Yojna to distribute tablets/smartphones to eligible students.
Under the Uttar Pradesh start-up policy 2020, start-ups in areas such as agriculture, medicine, and energy are being promoted.
There are 50 incubators and 7,200 start-ups operational in the state.
Rs. 100 crore has been allocated for the Seed Fund to boost incubators and start-ups.
Rs. 60 crore has been proposed for the Uttar Pradesh Information and Technology and Start-up Policy.
Rs. 20 crore has been proposed for the Agriculture Accelerator Fund.
Uttar Pradesh ranked first in the creation of employment under MGNREGA, with the creation of 2,629,000 Person Days of employment in 2022-23.
Under the new Uttar Pradesh Tourism Policy 2022, a target has been set to invest Rs. 10 lakh crore and create 20 thousand jobs in the next 5 years.
Under the Mukhyamantri Shikshuta Protsahan Yojna (CM Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme), the target has been set to train 31 thousand youths.
Social Security and Labour Welfare
Under the Old Age/Farmers Pension Scheme, a budget of Rs. 7,248 crore has been proposed for the financial year 2023-24.
Under the Prime Minister Svanidhi Yojna, Uttar Pradesh ranked first in loan distribution, distributing Rs. 1,190.49 crore to 10.33 lakh street vendors.
Under the Death and Disability Help Scheme for workers, in case of death at the workplace, workers will be paid Rs. 5 lakh. In case of permanent disability, Rs. 4 lakh will be provided, and in case of partial disability, Rs. 3 lakh will be given.
Infrastructure
In the financial year 2023-24, Rs. 235 crore has been proposed for the first phase of the new schemes of Jhansi Link Expressway and Chitrakoot Link Expressway.
The International Film City is being established by the Yamuna Expressway Industrial Development Authority.
The Ganga Expressway, spanning 594 km from Meerut to Prayagraj, is under construction with a cost outlay of Rs. 36,230 crore.
The Purvanchal Expressway is operational, and 56 percent of the work (as of December 2022) on the Gorakhpur Purvanchal Link Expressway is complete.
Health and Medicine
Rs. 12,631 crore has been proposed for various schemes under the National Rural Health Mission.
Rs. 1,655 crore is proposed for the Pradhan Mantri Atmanirbhar Swasthya Bharat Scheme.
As per the recommendation of the 15th Finance Commission, Rs. 407 crore will be spent in the financial year 2023-24 for the conversion of rural sub-health centers and Primary Health Centers (PHCs) into Health and Wellness centers.
Rs. 320 crore is allocated for the Prime Minister Matru Vandana Yojna, and Rs. 250 crore is proposed for the Aayushman Bharat Mukhyamantri Jan Arogya Abhiyan.
Under the “One District, One Medical College” Scheme, 45 districts have been covered with a medical college. Fourteen new medical colleges are under construction, and in 16 unserved districts, medical colleges are being established on the basis of a PPP (Public-Private Partnership) model.
Infrastructure and Industrial Development
By improving its rank by 12 places, Uttar Pradesh ranks 2nd in the Ease of Doing Business in India. It is placed in the “Achievers” category.
In order to attract investment in various sectors like IT/ITES, data centers, ESDM, defense and aerospace, electric vehicles, warehousing and logistics, tourism, textiles, MSME, etc., almost 25 policies have been formulated.
A decision has been taken to develop industrial corridors along the expressways to create 5 lakh employment opportunities.
Rs. 25 crore has been proposed for the establishment of Pharma Parks.
Under the new MSME Policy 2022 declared by the State Government, a 15 percent annual growth rate in employment has been proposed.
For the promotion of ODOP (One District One Product) and handicraft product marketing, Rs. 200 crore has been proposed for the establishment of a Unity Mall.
Rs. 21,159.62 crore has been proposed for the construction of roads and bridges.
Under the Mukhyamantri Samagra Gram Vikas Scheme, roads were built in 181 revenue villages.
Irrigation and Water Resource
The total geographic area of the state is 240.93 lakh hectares. Out of this, 188.40 lakh hectares are arable land, and agricultural activities are carried out on 165.42 lakh hectares of land.
Irrigation facilities are made available in approximately 99 lakh hectares through a 75090 km long canal system, 34316 government tube wells, 29 pump canals, and other means.
In the financial year 2023-24, Rs. 2803 crore has been proposed for flood control and water drainage.
Under the Jal Jeevan Mission, Rs. 25,350 crore has been provisioned for 2023-24.
Under the Rajya Grameen Payjal Programme, the target has been set to complete 188 projects with a total cost of Rs. 455.15 crore.
Civil Aviation
Presently, 9 airports, including 3 international ones, are operational.
International airports are under construction in Jewar and Ayodhya.
In the coming years, 5 international and 16 domestic airports will be operational.
Energy
The Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme has been initiated to enhance efficiency and capability, with a proposed budget of Rs 6,500 crore.
The average daily production availability was 3,766 MW in 2019-20, 3,816 MW in 2020-21, and 3,998 MW in 2021-22.
Furthermore, a budget of Rs 317 crore has been allocated for the Uttar Pradesh Solar Energy Policy 2022, and Rs 45 crore for the Uttar Pradesh State Bio Energy Policy 2022.
Housing and Urban Planning
Rs. 3,000 crore has been proposed for the Mukhyamantri City Expansion/New City Incentive Scheme.
A budget of Rs 585 crore for the Kanpur metro and Rs 465 crore for the Agra metro has been proposed for the financial year 2023-24.
Additionally, Rs 100 crore has been earmarked for Metro Rail Projects in Varanasi, Gorakhpur, and other cities.
For the grand organization of the Maha Kumbha in 2025, Rs 621.55 crore was proposed in 2022-23. However, the upcoming budget allocates Rs 2,500 crore for this purpose.
Planning
Under the Accelerated Economic Development Plan, a budget of Rs 1,500 crore has been proposed for new projects in the financial year 2023-24.
Furthermore, Rs 600 crore has been allocated for the Bundelkhand Special Plan, and Rs 525 crore for the Purvanchal Special Plan.
Panchayati Raj
Under the Swachha Bharat Mission (Grameen) for the year 2023-24, the target has been set to construct 665,473 individual toilets and implement plastic waste management in 330 development blocks. A budget of Rs 2,288 crore has been proposed for this scheme.
In addition, under the Rastriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan Yojana, Rs 622 crore has been allocated for capability enhancement, training, and the availability of organizational structures in Panchayats.
Agriculture and Allied Sector
To train farmers in the latest techniques, an innovative program called “The Million Farmer’s School” is being organized throughout the entire province.
For the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture Scheme, a budget of Rs 631.93 crore has been allocated.
An allocation of Rs 55.60 crore has been made for the Uttar Pradesh Millets Revival Scheme.
Furthermore, Rs 20 crore was proposed for the Agritech Start-up Scheme in four agricultural universities.
A provision of Rs 50 crore is proposed for the establishment of Mahatma Buddha Agricultural and Scientific University in Kushinagar.
An arrangement of approximately Rs 35 crore is proposed for infrastructure development in Agricultural Universities in Kanpur, Ayodhya, Banda, and Meerut.
Teaching and learning activities have commenced in the Agriculture College (WAMPS) in Azamgarh under Acharya Narendra Dev University of Agriculture and Technology, Ayodhya. Construction work is also in progress for the establishment of Agriculture College (WAMPS) in Gonda district.
A budget of Rs 25 crore has been proposed for the implementation of the Uttar Pradesh Dairy Development and Dairy Product Promotion Policy 2022.
For the implementation of the Nand Baba Dairy Mission, a budget of Rs 61.21 crore has been proposed for the financial year 2023-24.
To address the issues of destitute and helpless cattle, a target has been set to construct 187 large Gau-Sanrakshan Kendras, of which 171 kendras have been completed.
Under the Prime Minister Matsya Sampada Scheme, Rs 257.50 crore has been proposed for a wholesale fish market.
Additionally, Rs 100 crore has been proposed for the Uttar Pradesh Food Processing Industry Policy 2022.
Furthermore, to attract investment and maximize job creation in the textile sector, the Uttar Pradesh Textile and Garmenting Policy 2022 has been formulated.
Education
A budget of Rs 20,255 crore has been proposed for the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA).
Under Operation Kayakalp, primary and higher primary schools operated by the Basic Education Council are being developed into smart schools through infrastructure development, with Rs 1,000 crore proposed in the budget for 2023-24.
Additionally, Rs 510 crore has been allocated for the implementation of the new scheme, PM Shree (Prime Minister School for Rising India), aided by the central government.
For higher education in the state, there are currently 19 State Universities, 1 open university, 1 Deemed university, and 30 private universities in operation.
Both Lucknow University and Gorakhpur University have achieved A-Double plus NAAC ranking.
Furthermore, new State Universities are being established, including Maa Vindhyavasini State University (Rs. 50 crore) in Vindhyachal Dhaam Zone, Maa Paateshwari Devi State University (Rs 50 crore) in Devipatan Zone, and a State University (Rs. 50 crore) in Muradabad Zone.
Sports
A budget of Rs. 300 crore has been proposed for the Major Dhyan Chanda Sports University in Meerut district.
Additionally, Rs. 20.50 crore is proposed for Sports Colleges in Saharanpur, Fatehpur, and Balia.
Culture and Religious Works and Tourism
The Vedic Science Centre is being established on the Banaras Hindu University campus.
In the Mirzapur district, the process of developing a triangular parikrama path for the restoration and beautification of the famous Maa Vindhyavasini Devi Temple, Maa Ashtabhuji Devi Temple, and Kali Khoh Temple is in progress.
There is a proposal to establish a Bhajan Sandhya Sthal in the Prayagraj district, similar to Ayodhya and Chitrakoot districts.
There is also a proposal to establish a Veda Science Study Center in the famous Taposthali Naimisharanya in Sitapur district.
In the year 2022, more than 24.87 crore tourists arrived in Uttar Pradesh, out of which more than 4.10 lakh were foreign tourists.
Under the Mukhyamantri Paryatan Samvardhan Scheme, tourist places are being developed with a fund of Rs. 300 crore.
The Spiritual Circuit scheme includes the tourism development of Gorakhpur-Devipatan-Dumariaganj and integrated tourism development of Jewar-Dadri-Secunderabad-Noida-Khurja-Banda. Additionally, approved schemes for tourism development of Govardhan in Mathura district are being implemented.
A provision of Rs. 50 crore is proposed in the current financial year for the integrated tourism development of the Shakti Peeth Maa Shakumari Devi Temple in Saharanpur.
Under the Tourism Policy of 2018, a provision of Rs. 45 crore is proposed for the promotion of tourism units.
Furthermore, there is a provision of Rs. 10 crore for the integrated tourism development of Shukrateerth Dham in Muzzaffarnagar.
A sum of Rs. 2.50 crore is proposed for the development of Shri Naimisharanya Dham Teerth in Sitapur by the Development Council.
Lastly, Rs. 2.50 crore is proposed for the establishment of the Uttar Pradesh Eco Tourism Board in Lucknow.
Allocation of Funds under Major Schemes (2023-24)
| Sr. No. | Scheme/ Programme/Policy | Allocated Fund (in ₹ crore) |
| 1. | Mukhyamantri Kanya Sumangla Yojna | 1050 |
| 2. | Swami Vivekanand Yuva Sashaktikaran Yojna | 3600 |
| 3. | Seed Fund | 100 |
| 4. | Uttar Pradesh IT & Start-up Policy | 60 |
| 5. | Old Age / Kisan Pension | 7248 |
| 6. | Divyang Pension | 7248 |
| 7. | Mukhyamantri Jan Arogya | 100 |
| 8. | Mukhyamantri Durghatna Bima Yojna | 12 |
| 9. | Jhansi Link Express-way & Chitrakoot Link Express-way | 2350 |
| 10. | Bundelkhand Express-way | 550 |
| 11. | Gorakhpur Link Express-way | 200 |
| 12. | National Rural Health Mission | 12631 |
| 13. | PM Aatmanirbhar Swasthya Yojna | 1655 |
| 14. | ODOP Unity Mall | 200 |
| 15. | State Road Fund (Maintenance & Construction) | 3000 + 2500 |
| 16. | Flood Control & Water Supply | 2803 |
| 17. | Jal Jeevan Mission | 25350 |
| 18. | Uttar Pradesh Solar Energy Policy, 2022 | 317 |
| 19. | Mahakumbh Mela | 2500 |
| 20. | AMRUT 2.0 | 5616 |
| 21. | Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 | 2707.86 |
| 22. | Akanshi Nagar Yojna | 100 |
| 23. | Accelerated Economic Development Scheme | 1500 |
| 24. | Bundelkhand Special Plan | 600 |
| 25. | Purvanchal Special Plan | 525 |
| 26. | PM Awas Yojna (Grameen) | 9000 |
| 27. | PM Gram Sadak Yojna | 5966 |
| 28. | Mukhyamantri Awas Yojna | 1203 |
| 29. | Rashtriya Krishi Vikash Yojna | 984.54 |
| 30. | National Crop Insurance Scheme | 753.70 |
| 31. | PM Matsya Sampada Yojna | 257.50 |
| 32. | Uttar Pradesh Food Processing Industry Policy, 2022 | 100 |
| 33. | Uttar Pradesh Electronics Manufacturing Policy | 401 |
| 34. | Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan | 20555 |
| 35. | Operation Kayakalp | 1000 |
| 36. | Digital Library in Gram Panchayats | 300 |
| 37. | Project Alankar | 500 |
| 38. | Kaushal Vikash Mission | 150 |
| 39. | Mukhyamantri Shikshuta Prashikshan Yojna | 70 |
| 40. | Khelo India University Games | 30 |
| 41. | Sports Development Fund | 25 |
| 42. | Mukhyamantri Paryatan Samvardhan | 300 |
| 43. | Tourism Policy, 2018 | 45 |
| 44. | Buddha Circuit | 40 |
| 45. | Social Forestry Scheme | 600 |
| 46. | Green India Mission | 100 |
| 47. | Eco-Tourism | 10 |
| 48. | Annapurti Yojna | 21791.25 |
| 49. | Ujjawala Yojna | 3047 |
| 50. | Rashtriya Poshan Abhiyan | 455.52 |
